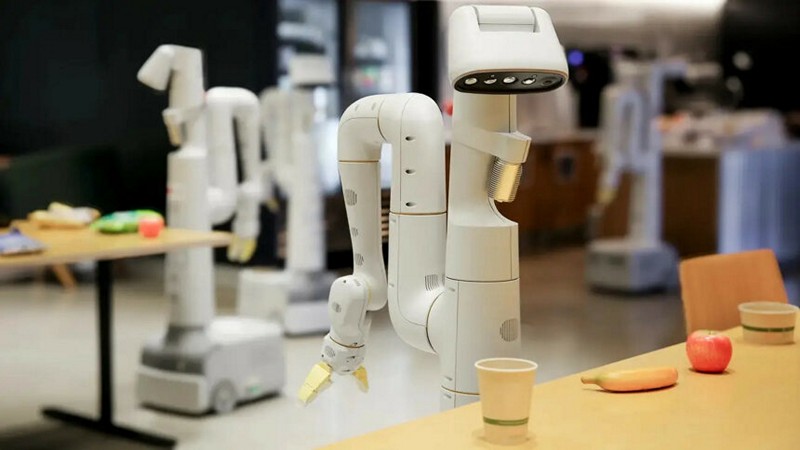

Google’s DeepMind is taking strides towards integrating AI-powered robots into domestic life with a set of advances designed to make these machines more human-like. In a move toward ensuring safety, a peculiar concept called the “robot constitution” has been introduced, drawing inspiration from Isaac Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics. How effective is the robot constitution in ensuring the safe operation of AI-powered robots, in what ways does AutoRT contribute to imbuing robots with a high-level understanding of the world, and what impact might these advancements have on the feasibility of integrating AI-powered robots into daily household activities?
Top Stories This Week
- Google Developing Robot Constitution To Ensure Safe Use In Homes
- Google Inclines Towards Taiwanese Manufacturers For Next-Gen Tensor & AI Chips
- Turn Wasted Wind Power Into Green Hydrogen And Save UK Billions: Study
- UK Government Approves Controversial $2.5B Project For ‘Carbon Negative’ Power Plant
- AI To Hit 40% Of Jobs And Worsen Inequality, IMF Says
- New Bluetooth Vulnerability Allows Takeover Of iOS, Android, Linux, And MacOS Devices
- Beyond Lithium-Ion: Exploring Next-Gen Battery Technologies
- Samsung Is Setting Up a No-Human, All-AI Chip Factory
- Luminescent Sensor Detects ‘Forever Chemical’ Pollution In Water
- AI Challenges Notion That All Fingerprints Are Unique
- The OWASP AI Exchange: An Open-Source Cybersecurity Guide To AI Components
Hardware Business News
Google Inclines Towards Taiwanese Manufacturers For Next-Gen Tensor & AI Chips

In a surprising move, Google is reportedly altering its semiconductor sourcing strategy for the upcoming Tensor lineup and AI chips, opting for Taiwanese manufacturers instead of its longstanding partnership with Samsung Foundry. The decision is expected to bring a fresh approach to Google’s mobile System on a Chip (SoC) segment, offering potential advantages in terms of chip designs and performance. What factors led Google to shift away from Samsung Foundry and turn to Taiwanese manufacturers for its next-gen Tensor lineup and AI chips, how does Google’s investment in KYEC’s facilities contribute to the manufacturing process, and what unique advantages could this collaboration offer in terms of chip designs and performance?
Turn Wasted Wind Power Into Green Hydrogen And Save UK Billions: Study

A recent report from London think tank Policy Exchange suggests that the UK has the potential to save billions of pounds annually by leveraging excess wind power for the production of green hydrogen. The report argues that the UK’s exceptional wind turbine fleet has outpaced its electricity grid, resulting in substantial curtailment fees paid to wind farm owners. By redirecting this excess wind power towards green hydrogen production, the UK could address both the issue of curtailment costs and contribute to the growth of its nascent hydrogen economy. How has the imbalance between the UK’s wind turbine fleet and its electricity grid led to significant curtailment fees, how do projections indicate a rise in curtailment costs to £3.5bn annually by the end of the decade, and what role does excess wind power play in this scenario?
UK Government Approves Controversial $2.5B Project For ‘Carbon Negative’ Power Plant

The UK government has granted approval for a £2 billion project that involves retrofitting carbon capture units onto two generators at Drax’s power station in Yorkshire. The aim is to create a carbon negative wood-burning power plant, capable of preventing 4 million tons of carbon pollution annually. The carbon captured will be stored under the North Sea to mitigate its impact on global warming. How does the “carbon negative” wood-burning power plant concept work, what role does bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS) play in achieving carbon negativity, and despite gaining government approval, why are some climate experts critical of the BECCS technology and the use of biomass, citing concerns related to its effectiveness in mitigating climate change and potential environmental impacts?
AI To Hit 40% Of Jobs And Worsen Inequality, IMF Says
Artificial intelligence is predicted to influence nearly 40% of all jobs, with potential consequences for overall inequality, according to a new analysis by the International Monetary Fund. Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva emphasized that, in most scenarios, AI might exacerbate inequality, leading to a troubling trend that policymakers should address to prevent social tensions. What are the key findings of the IMF analysis regarding the impact of AI on jobs, what are the potential consequences of AI on overall inequality, and how does the analysis highlight the disproportionate effects on different demographic groups, such as higher-income versus lower-income workers?
Hardware Engineering News
New Bluetooth Vulnerability Allows Takeover Of iOS, Android, Linux, And MacOS Devices

A recently discovered Bluetooth security flaw has raised concerns as it leaves keyboards susceptible to injection attacks, potentially allowing threat actors to gain control over devices running Android, Linux, macOS, and iOS. The flaw, identified as CVE-2023-45866, has prompted Google, Microsoft, Linux (BlueZ), and Apple to release fixes over the past six weeks. What are the key details of the Bluetooth security flaw (CVE-2023-45866), how did security researcher Marc Newlin discover the flaw, and in what ways does the Bluetooth vulnerability extend to different platforms?
Beyond Lithium-Ion: Exploring Next-Gen Battery Technologies

The surge in demand for clean energy solutions has illuminated the inherent limitations of lithium-ion batteries, propelling the electronics industry into an era of innovative exploration for sustainable alternatives. Beyond lithium-ion lies a realm of experimental materials and novel applications designed to alleviate concerns related to resource scarcity, environmental impact, and soaring costs. How do solid-state batteries tackle safety concerns associated with conventional lithium-ion batteries, what advantages do they bring in terms of lifecycle and safety features for applications in electronics and electric vehicles, and how could these batteries significantly improve energy efficiency in various applications, including hearing aids and uninterruptible power supplies?
Samsung Is Setting Up a No-Human, All-AI Chip Factory

Samsung Electronics, a global tech powerhouse, is on the brink of transforming the semiconductor industry with its audacious plan to achieve complete automation of chip manufacturing by 2030. In a visionary leap, Samsung envisions the establishment of an artificial intelligence fab, where the entire chip production process will be orchestrated by smart sensors, significantly reducing human intervention. How does Samsung’s “Smart Sensing System” leverage artificial intelligence to monitor and optimize semiconductor production processes in real time, what potential implications and challenges arise, particularly concerning job displacement and the societal impact on the semiconductor industry workforce, and in what ways does Samsung’s focus on in-house development of smart sensors contribute to the company’s goal of technological self-sufficiency?
Hardware R&D News
Luminescent Sensor Detects ‘Forever Chemical’ Pollution In Water

A collaborative effort between researchers at Birmingham University and Germany’s Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM) has led to a ground-breaking approach for detecting pollution caused by per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), often referred to as ‘forever chemicals.’ PFAS, known for their widespread use in various industries and environmental persistence, pose a significant threat due to their non-degradable nature. How does the newly developed luminescent sensor, utilizing metal complexes, detect ‘forever chemicals’ like perfluorooctanoic acid, what advantages does this approach offer over traditional, time-consuming detection methods, and how could this innovative technology be instrumental in on-site spill monitoring and determining the presence of PFAS in drinking water, contributing to environmental and public health protection?
AI Challenges Notion That All Fingerprints Are Unique

Researchers at Columbia University have thrown a significant challenge at a fundamental principle of forensic science – the uniqueness of fingerprints. Utilizing an AI-based deep contrastive network, the team discovered that the system could remarkably identify prints from different fingers of the same person, challenging the conventional belief that intra-person fingerprints are distinct and unmatchable. How did the AI-based deep contrastive network manage to identify prints from different fingers of the same person, what are the potential consequences for forensic investigations, and how might this unorthodox challenge to fingerprint uniqueness impact the reopening of cold cases or the reassessment of existing forensic evidence?
Open-Source Hardware News
The OWASP AI Exchange: An Open-Source Cybersecurity Guide To AI Components

In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence adoption, the increasing integration of AI tools raises concerns about cybersecurity. Addressing this, the Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) presents the AI Exchange – a collaborative initiative facilitating the global sharing of AI security standards, regulations, and knowledge. As organizations grapple with the intricacies of securing AI, OWASP AI Exchange emerges as a pivotal resource, providing insights into threats, vulnerabilities, and controls. How does the OWASP AI Exchange contribute to enhancing AI security standards, what specific features, such as the AI Exchange Navigator, make it a valuable resource for practitioners in the ever-changing AI landscape, and with AI-specific security threats expanding, how does OWASP AI Exchange guide organizations in identifying and mitigating risks throughout the AI software development lifecycle?


