A new report by Goldman Sachs economists has predicted that up to 18% of jobs worldwide could be automated by the latest wave of artificial intelligence, with the effects felt more deeply in advanced economies than emerging markets. It is believed that this is partly because white-collar workers are seen to be more at risk than manual labourers, with administrative workers and lawyers expected to be most affected. However, the economists note that technological innovation that initially displaces workers has historically also created employment growth over the long haul. In addition, widespread adoption of AI could ultimately increase labour productivity and boost global GDP by 7% annually over a 10-year period. How will AI automation impact the workforce, what kind of jobs are most at risk, and can technological innovation lead to employment growth over the long term?
Top Stories This Week
- 300 Million Jobs Could Be Affected By Latest Wave Of AI
- NASA Funds First Wearable To Measure Muscle Atrophy
- With Security Copilot, Microsoft Brings The Power Of AI To Cyberdefense
- Ford Expects To Lose $3 Billion On Evs This Year
- US-China Chip War: Japan Plans To Restrict Some Equipment Exports
- Remembering Gordon Moore: The Technology Pioneer Who Revolutionised The Industry
- Lack Of Transparency Over Police Forces’ Covert Use Of Predictive Policing Software
- New Vulnerabilities Found In Industrial Control Systems Of Major Vendors
- Ultrasound Hacks: The Hidden Dangers Of Voice-Controlled Devices
- New Textile Sensor Breakthrough: Detecting Strain With Greater Sensitivity
- Is RISC-V Poised To Benefit From Arm’s Licensing Changes?
Hardware Business News
NASA Funds First Wearable To Measure Muscle Atrophy
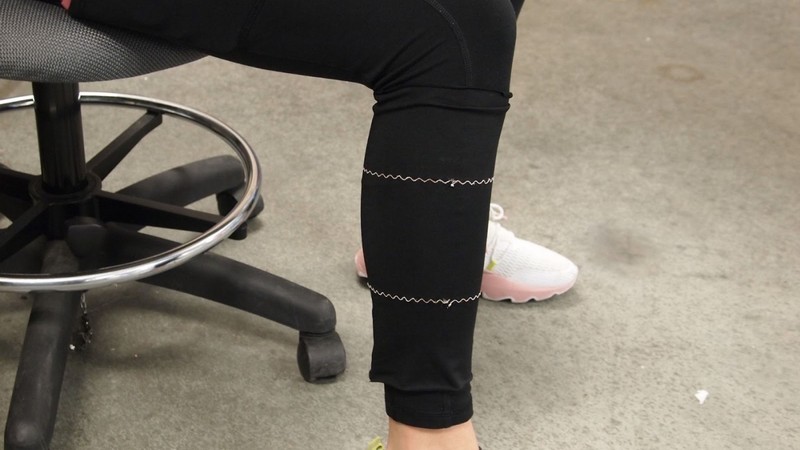

NASA has funded the development of a wearable device designed to detect and monitor muscle atrophy in astronauts during long-duration space missions. Exposure to microgravity can cause astronauts to lose up to 20% of their muscle mass, making it necessary for them to exercise for two or more hours daily while in space. The new wearable, developed by researchers at Ohio State University, looks like a blood pressure cuff and contains two loops of electrically conductive threads that stretch and contract in response to the wearer’s calf muscle. How could this wearable help NASA monitor astronauts during long-duration space missions, what are some potential applications of this wearable on Earth, and what other methods are NASA exploring to prevent muscle atrophy in astronauts?
With Security Copilot, Microsoft Brings The Power Of AI To Cyberdefense
Microsoft has announced the launch of Security Copilot, a next-generation AI-powered cybersecurity tool that promises to enhance the work of security professionals and improve their understanding of the threat landscape. The new product is designed to simplify complexity, amplify capabilities, and augment the expertise of security teams by summarising and making sense of threat intelligence, correlating and summarising data on attacks, prioritising incidents and recommending the best course of action. How does Security Copilot use AI to augment the work of security professionals, how will Security Copilot help address skills shortages in cybersecurity, and what kind of impact will Security Copilot have on the future of cybersecurity?
Ford Expects To Lose $3 Billion On EVs This Year

Ford, one of the long-time automakers, has reported that it will lose around $3 billion on its sales of electric vehicles to consumers this year. Despite this, the company still expects to hit its profit targets for the year, which range between $9 billion and $11 billion. However, it remains far less profitable than EV leader Tesla, which reported a 22% profit margin in the fourth quarter. Ford expects its EVs to start making money soon, going from a 40% operating loss margin last year to an 8% profit margin by the end of 2026. The company also plans to bring global production of its EVs to a 2 million annual rate by the end of that year. The report reveals Ford’s approach towards making a profit on electric cars, as well as its projection for future growth. In light of this, what factors led to Ford’s $3 billion loss on its sales of electric vehicles, will Ford be able to hit its EV profit goals and catch up to Tesla, and what changes can Ford make to improve the profit margins on its EVs?
US-China Chip War: Japan Plans To Restrict Some Equipment Exports
Japan is planning to impose export restrictions on 23 types of semiconductor manufacturing equipment, joining the US and the Netherlands in taking measures to protect their respective national security interests. The move follows a bitter dispute between the US and China, with semiconductors being at the centre of the controversy. While Japan did not explicitly mention China or the US in its announcement, the decision is likely to have significant implications for China’s tech industry. What types of semiconductor manufacturing equipment will be affected by Japan’s new policy, will these restrictions harm Japan’s relationship with China, and how might this policy change affect the global supply chain of semiconductors?
Hardware Engineering News
Remembering Gordon Moore: The Technology Pioneer Who Revolutionised The Industry

Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Intel and a pioneer in modern computing, recently passed away, leaving behind an immeasurable impact on the technology industry. His contributions, ranging from memory chips and microprocessors to his famous prediction, Moore’s Law, revolutionised the industry, leading to cost reduction and the development of the X86 microprocessor. Moore’s legacy extends beyond his work at Intel to his commitment to education, scientific research, philanthropy, conservation, and the development of clean energy technologies, all achieved through constructive confrontation. Despite his global recognition, Moore remained humble about his beginnings and the journey to success.
Lack Of Transparency Over Police Forces’ Covert Use Of Predictive Policing Software

A recent report by The Citizens reveals that UK police forces are using blanket exemption clauses to withhold information on the use of covert software that monitors citizens’ behaviour, citing national security and law enforcement. Tech companies like Palantir, NSO Group, QuaDream, Dark Matter, Gamma Group and Dataminr, a social media monitoring tool, have all been exempted from disclosure by the police, citing potential operational harm. Dataminr has been linked to monitoring Black Lives Matter and Muslim rights activism, with US law enforcement using it to prevent BLM protests. However, recent research shows that Dataminr produces results that reflect its clients’ politics, business goals and ways of operating, and not just neutral observational data. What are the consequences of this on citizens’ rights to protest, how can the government ensure transparency and accountability in the use of covert software by law enforcement, and can technology companies guarantee the neutrality of their software?
New Vulnerabilities Found In Industrial Control Systems Of Major Vendors

The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has issued advisories on 49 vulnerabilities found in eight industrial control systems (ICS) used in critical infrastructure sectors, including energy, transportation, and manufacturing. The vulnerabilities identified by CISA are remotely exploitable, involve low attack complexity, and allow attackers to take control of affected systems, manipulate and modify settings, escalate privileges, bypass security controls, steal data, and crash systems. What are the potential implications of these vulnerabilities on critical infrastructure sectors, how can organisations mitigate the risks posed by these vulnerabilities, and what steps can governments take to prevent these types of cyberattacks?
Hardware R&D News
Ultrasound Hacks: The Hidden Dangers Of Voice-Controlled Devices
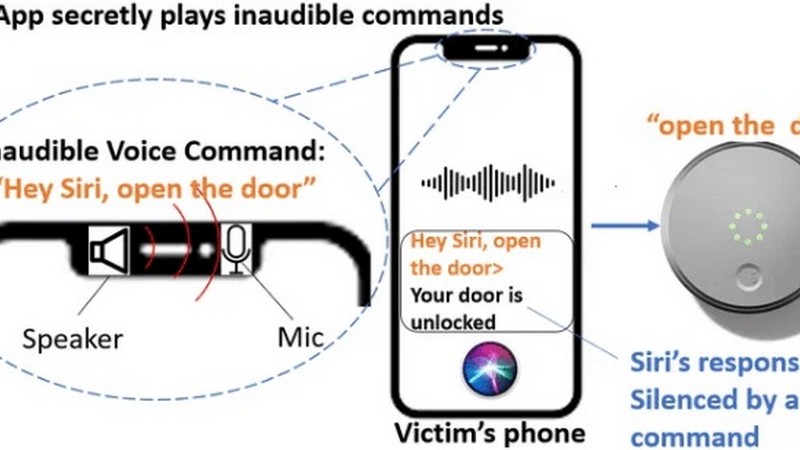
Researchers recently demonstrated how hackers can exploit Near-Ultrasound Inaudible Trojan (NUIT) to send inaudible ultrasound commands to voice-controlled systems like Alexa and Siri, raising concerns over privacy, surveillance, and data breaches involving personal information. This hardware design issue highlights the need for engineers to develop solutions to defend against such attacks and improve devices’ frequency response to filter out inaudible commands, potentially necessitating a software fix to address ambient noise interference. What challenges do voice-activated systems present, what did the researchers demonstrate, and how can such attacks be mitigated?
New Textile Sensor Breakthrough: Detecting Strain With Greater Sensitivity
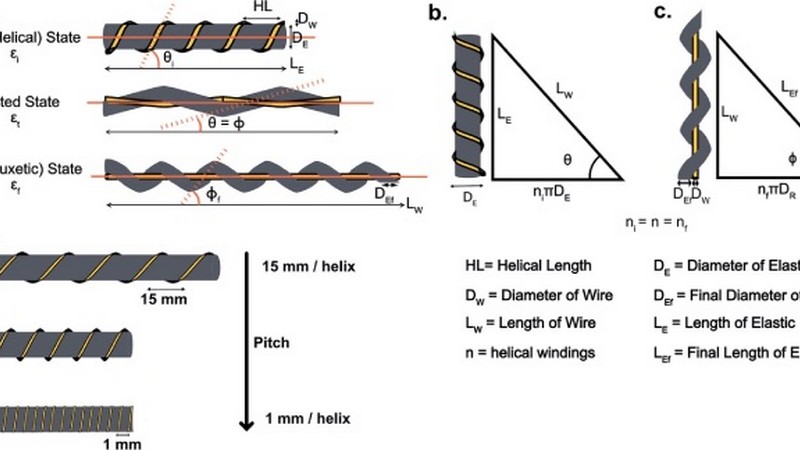
Researchers from ETH Zurich have made significant progress in the field of wearable electronics by developing a new textile sensor with greater sensitivity for detecting strain. This breakthrough was made possible by taking advantage of flexible technologies, conductive fibers, and capacitive strain gauges while also addressing challenges such as the Poisson effect and the need for auxetic structures like the helical thread structure with a negative Poisson ratio. The resulting passive sensors can wirelessly communicate with other devices, allowing for features like early fatigue detection and stride length and duration detection. What challenges do textile sensors face, what did the researcher develop, and how could they be used in the future?
Open-Source Hardware News
Is RISC-V Poised To Benefit From Arm’s Licensing Changes?
Amid industry challenges and after facing financial difficulties, ARM is considering different ways to increase its revenue, such as the possibility of raising the license price and expanding the license scope. This comes after the NVIDIA acquisition and with the ongoing semiconductor trade war. ARM China, Qualcomm, and other semiconductor vendors are looking at alternative business models, including the adoption of RISC-V and open-source designs to break from ARM’s monopoly. What challenges has ARM been facing, what exactly has been reported, and why could this be the break RISC-V needs?