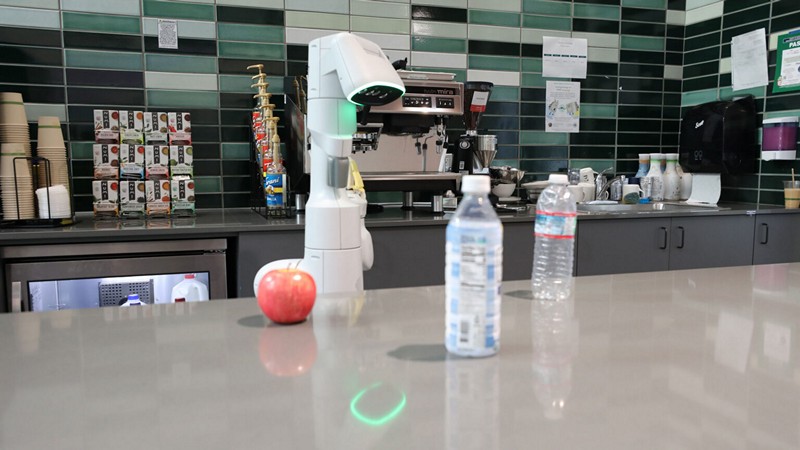
In the pursuit of making robots safer and more efficient, engineers at Princeton University and Google have devised a ground-breaking method to teach robots when to seek assistance. While modern robots excel in sensing their environment and responding to language, the ability to recognize what they don’t know is crucial for preventing unsafe or unreliable behaviour. This innovative approach involves quantifying the uncertainty in human language, using large language models (LLMs) similar to ChatGPT. How does the new method address a fundamental challenge in robotics by enabling robots to recognize and act on uncertainties in complex tasks, in what ways might allowing users to set specific success targets based on uncertainty thresholds enhance the adaptability and reliability of robots across different scenarios, and what impact could this breakthrough have on the future development of robotics, especially in terms of improving safety and efficiency in real-world applications?
Top Stories This Week
- How Do You Make A Robot Smarter? Program It To Know What It Doesn’t Know
- Sensor Tech Start-Up Seeks Investment To Target The ‘Detection Gap’
- US, UK, Others Agree ‘Secure By Design’ AI
- Demand For AI Sparks Increase In Data Centre Server Spending, Even As Shipments Fall
- Chip Packaging R&D Gets $3B US Boost To Turn Tide
- UK Space Agency Funds Work To Replace Russian Components On Mars Rover
- AI Doesn’t Cause Harm By Itself. We Should Worry About The People Who Control It
- How Are Microchips Made? From Silicon Crystals To Integrated Circuits
- Cutting-Edge Wearable Device With Gold Nanowires To Enhance Disease Diagnosis
- Smart Aid Kit Uses AI To Remotely Diagnose And Manage Health Conditions
- US Could Ban RISC-V Exports To China As Alibaba Develops 3072-Core RISC-V
Hardware Business News
Sensor Tech Start-Up Seeks Investment To Target The ‘Detection Gap’

UK-based sensor technology firm, Ladar Ltd, is on the brink of advancing its cutting-edge sensor suite platform with the goal of enhancing security and defense capabilities. Having received initial support through an EU-funded development project, Ladar is now actively seeking €3.5 million (US$3.8 million) in private funding to bring its Ladar sensor suite platform to fruition. How does Ladar’s sensor suite platform address the ‘detection gap’ in maritime security, particularly in near-surface and semi-submerged levels, where traditional radar technology falls short, in what ways can the integration of AI and machine learning algorithms enhance Ladar’s platform’s ability to find, classify, and track targets both above and below the ocean surface, and how does Ladar envision the deployment of its technology in military contexts?
US, UK, Others Agree ‘Secure By Design’ AI
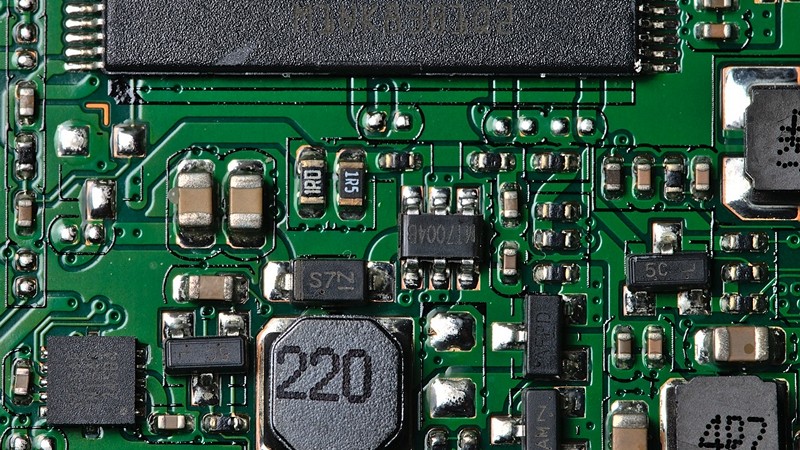

In a landmark move, the United States, United Kingdom, and a coalition of over a dozen countries have entered into a ground-breaking international agreement focused on strengthening cybersecurity for artificial intelligence (AI). This accord, hailed as the first detailed global initiative to safeguard AI from malicious actors, emphasizes the creation of AI systems that are inherently secure. How do the newly established guidelines for secure AI system development aim to address the pressing need for international cooperation in enhancing AI cybersecurity, what specific challenges does the agreement tackle concerning the potential exploitation of AI technology by malicious actors, and how does it propose to safeguard AI systems from cybersecurity threats?
Demand For AI Sparks Increase In Data Centre Server Spending, Even As Shipments Fall
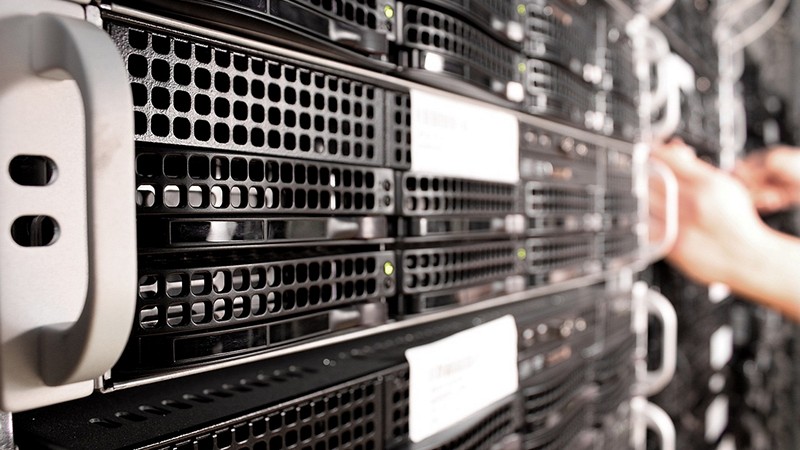

As data centre server shipments face a potential 20% decline this year, a surprising trend emerges in the tech industry — the demand for more sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI) hardware is leading to increased revenues for companies involved in AI-centric server technologies. Omdia’s latest Cloud and Data Centre Market Update highlights a phenomenon called “hyper heterogeneous computing,” where servers are equipped with multiple silicon chips to handle AI workloads, driving up their costs. How does the trend of hyper heterogeneous computing reflect the evolving landscape of data centre technologies, how are major players like Nvidia, Microsoft, and Meta leading the way in adopting these technologies, and what impact does this have on more traditional server manufacturers?
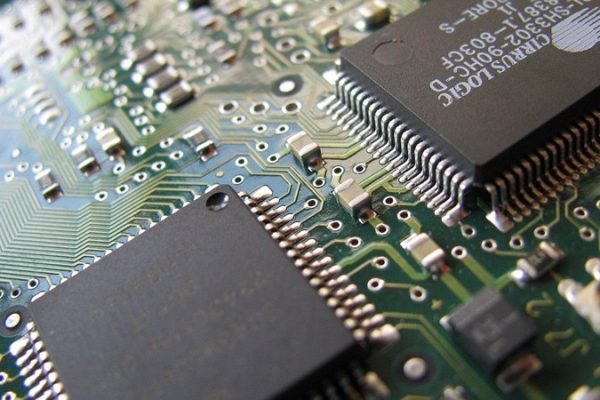
Chip Packaging R&D Gets $3B US Boost To Turn Tide
In the competitive landscape of semiconductor technology, the United States grapples with a notable shortfall in advanced chip packaging capabilities, a crucial element for efficient AI processors and GPUs. In recognition of this, the Biden administration has allocated $3 billion in funding to NAPMP, aiming to propel the US into the forefront of advanced packaging technologies. The initiative seeks to address challenges such as high-volume manufacturing and the implementation of the latest advancements in silicon technology. How does the US’s current deficiency in advanced chip packaging impact its ability to compete in the global semiconductor market, what specific areas will be prioritized to accelerate advancements in chip packaging, and how might this initiative address existing challenges in the industry?
Hardware Engineering News
UK Space Agency Funds Work To Replace Russian Components On Mars Rover
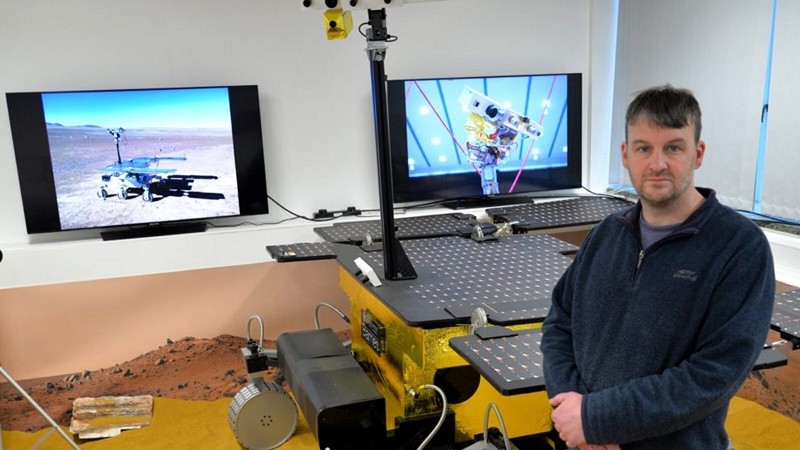

In a strategic move to uphold its commitment to space exploration, the UK Space Agency has allocated an additional £10.7 million for the replacement of a Russian-made instrument on the Rosalind Franklin rover. Originally set to launch in 2022 as part of a European Space Agency initiative, the collaboration with Russia’s space agency was terminated following the illegal invasion of Ukraine. The new funding will enable a UK team to substitute the Russian-built Infrared Spectrometer for ExoMars (ISEM) with a new instrument named Enfys, meaning ‘rainbow’ in Welsh. How does the replacement of the Infrared Spectrometer with the Enfys instrument contribute to enhancing the scientific capabilities of the Rosalind Franklin rover’s Mars mission, how does this funding boost strengthen the UK’s position in the global space exploration landscape, and what potential economic and technological impacts might arise from this investment?
AI Doesn’t Cause Harm By Itself. We Should Worry About The People Who Control It
OpenAI, a company founded by Silicon Valley heavyweights including Elon Musk and Peter Thiel, initially positioned itself as a non-profit charitable trust dedicated to developing artificial general intelligence (AGI) ethically for the benefit of humanity. However, its journey took a complex turn with the creation of a for-profit subsidiary, raising over $11 billion from Microsoft and intensifying the internal struggle between profit-making and doomsday concerns. How does OpenAI’s evolution from a non-profit organization to a for-profit subsidiary reflect the inherent contradictions in the tech industry, how does this fear of AI influence decision-making within organizations like OpenAI, and what impact does it have on the ethical development of AI technologies?
How Are Microchips Made? From Silicon Crystals To Integrated Circuits
Microchips, the unsung heroes powering our modern electronic devices, undergo a fascinating journey from silicon to sophisticated electronic components. Recognising the incredible history behind the microchip, in this article published by electropages, explore the complex process of how microchips are made, tracing their evolution from simple silicon wafers to intricate electronic circuits that drive daily-use appliances and advanced computing systems. How has the historical evolution of microchip manufacturing shaped the technological landscape and impacted the integration of microchips into various aspects of our lives, what challenges do engineers and scientists face in microchip fabrication, and what innovative solutions are being explored to push the boundaries of microchip technology?
Hardware R&D News
Cutting-Edge Wearable Device With Gold Nanowires To Enhance Disease Diagnosis
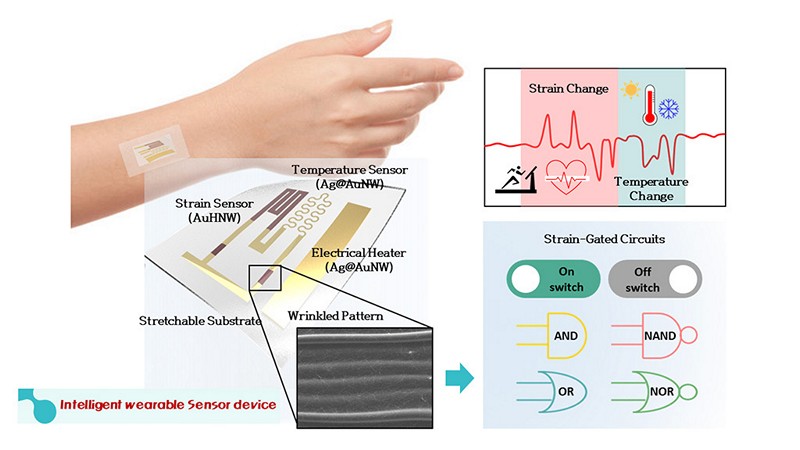
Gold, renowned for its stability, electrical conductivity, and biocompatibility, has long been a staple in the medical and energy sectors. Now, it’s taking centre stage in the realm of advanced wearable technology thanks to recent research from Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) that leverages gold nanowires to create an integrated wearable sensor capable of measuring and processing two bio-signals concurrently. How does the integration of gold and silver nanowires in wearable sensors address the challenges associated with simultaneously measuring multiple bio-signals, in what ways does the unique combination of bulk gold nanowires and hollow gold nanowires contribute to the seamless integration, stability, and versatility of the wearable sensor developed by the researchers at POSTECH, and how might the applications of this integrated wearable sensor extend beyond traditional healthcare settings?
Smart Aid Kit Uses AI To Remotely Diagnose And Manage Health Conditions
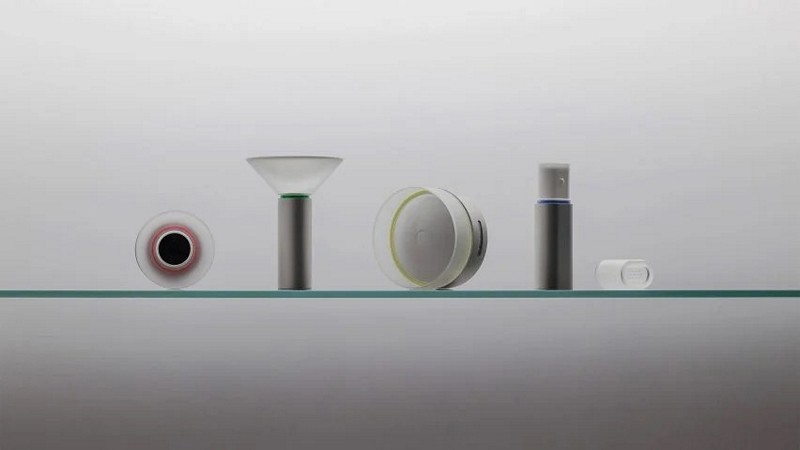

Design studios Map Project Office and Modem have unveiled a new concept for a diagnostics kit backed by artificial intelligence, redefining how individuals, particularly in underprivileged areas, can access healthcare. The Smart Aid Kit integrates generative AI with four sensors inspired by medical devices—a stethoscope, spirometer, ophthalmoscope, and skin scanner. By harnessing AI, this innovative kit allows users to perform basic self-triage, bridging the gap for communities without immediate access to healthcare services. How does the Smart Aid Kit, equipped with AI and four specialized sensors, address the crucial need for universal healthcare in underprivileged areas, what impact could it have on empowering individuals to manage their healthcare independently, and what challenges or opportunities could arise in implementing such a system on a broader scale?
Open-Source Hardware News
US Could Ban RISC-V Exports To China As Alibaba Develops 3072-Core RISC-V

As the U.S. tightens restrictions on China’s access to X86, Arm CPUs, and AI-related GPUs, the spotlight has shifted to the rapidly evolving RISC-V microarchitecture. While current bans do not include RISC-V, recent developments indicate that China is seizing this opportunity to propel its compute power. Notably, Alibaba has unveiled a 3,072-core RISC-V cloud server, signalling a shift from its earlier focus on Arm-based technology due to export bans. How might the U.S. respond to the significant advancements in cloud server processors and supercomputing, how could the existing rules on chip exports potentially provide a legal framework for addressing the open-source nature of RISC-V, and what challenges may arise in attempting to regulate such an architecture?