The ongoing global chip shortage has compelled manufacturers to venture into unconventional sources for electronic components. However, this pursuit of scarce components comes with a significant risk – the infiltration of counterfeit parts into the supply chain. In this article, Rob Moore, Sales Director at Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS), outlines the critical challenges posed by counterfeit electronics in the manufacturing industry. How has the chip shortage exacerbated the problem of counterfeit electronic components in manufacturing, what are the potential consequences for businesses and consumers if counterfeit parts infiltrate the supply chain, and what are the key strategies and quality control measures that EMS employs to ensure the authenticity of electronic components and safeguard against counterfeit products?
Top Stories This Week
- Dealing With Counterfeit Components
- Controversial Chip In Huawei Phone Produced On ASML Machine
- SiFive Lays Off Hundreds of RISC-V Developers
- Apple To Spend $1 Billion Per Year In AI To Catch Up
- Nvidia And AMD Plan To Launch Arm PC Chips As Soon As 2025
- How To Overcome 4 Common IIoT Adoption Challenges
- Busting The Automation Myths: 7 Reasons To Embrace Robotics
- UK Officials Use AI To Decide On Issues From Benefits To Marriage Licences
- Tiny Printed Dynamo Powers Bicycle Inner Tube’s Pressure Sensor
- Wearable Device Makes Memories And Powers Up With The Flex Of A Finger
- What Are RISC-V Chipsets And How Will They Redefine Next-Gen Wearable Tech
Hardware Business News
Controversial Chip In Huawei Phone Produced On ASML Machine
Recent revelations suggest that export restrictions on semiconductor manufacturing equipment may not have been sufficient to halt China’s advances in chipmaking. Despite broad export controls, Huawei introduced a 7-nanometer chip in its Mate 60 Pro, raising questions about the effectiveness of export restrictions and the mechanisms through which Chinese firms continue to advance. How did Huawei manage to develop advanced semiconductor chips, specifically a 7-nanometer chip, despite export restrictions on critical manufacturing equipment like ASML’s EUV machines, how has China’s government-supported chipmaking industry allowed it to bypass these restrictions, and what are the implications of the Biden administration’s new export controls on ASML’s sales to China?
SiFive Lays Off Hundreds of RISC-V Developers

SiFive, a prominent player in the RISC-V ecosystem, is currently undergoing a significant restructuring marked by extensive layoffs and a potential shift in its business focus. The company has reportedly laid off a substantial number of employees, primarily engineers, and is focusing on refocusing its global teams to meet fast-changing customer requirements. SiFive plans to offer both standard and custom products for various applications, including automotive, consumer electronics, data centres, artificial intelligence, high-performance computing, and wearables. What prompted SiFive to initiate a significant restructuring, leading to substantial layoffs of engineers and other personnel, how does SiFive plan to refocus its business strategy and product offerings to meet changing customer requirements, and what implications might this restructuring have for SiFive’s contributions to RISC-V standards and its competitive position within the semiconductor industry?
Apple To Spend $1 Billion Per Year In AI To Catch Up

Apple is reportedly ramping up its investment in generative artificial intelligence (AI) development, with plans to spend approximately $1 billion per year on enhancing its AI capabilities. While Apple already uses AI in various aspects of its products, it has yet to launch a generative AI product similar to those introduced by competitors like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon. support tools. Why is Apple significantly increasing its investment in generative artificial intelligence development, and how does it compare to its competitors in this space, what are some specific applications or areas where Apple plans to leverage AI, including potential integrations with Siri, Messages, and Apple Music, and who are the key executives leading Apple’s AI initiatives?
Nvidia And AMD Plan To Launch Arm PC Chips As Soon As 2025

Nvidia and AMD are reportedly gearing up to enter the market for Arm-based CPUs designed for Windows-based PCs, marking a potential shift in the competitive landscape for PC processors. While Microsoft has previously collaborated exclusively with Qualcomm for Arm-based versions of Windows, the entry of Nvidia and AMD into this domain could introduce new dynamics to the ecosystem. The move is aimed at challenging Intel, whose laptops have faced competition from Apple’s M1 and M2 chips. How does the entry of Nvidia and AMD into the market for Arm-based CPUs for Windows PCs impact the existing collaboration between Microsoft and Qualcomm for Arm-based Windows devices, what challenges has Intel faced in the wake of Apple’s M1 and M2 chips, and what are the specific plans or products in development that Microsoft, Nvidia, and AMD are working on?
Hardware Engineering News
How To Overcome 4 Common IIoT Adoption Challenges

Industrial IoT (IIoT) has gained significant traction for its ability to enhance intelligence, productivity, and asset management in industrial settings. It holds the promise of harnessing data generated by machines and components, enabling organizations to optimize performance and efficiency. Despite the substantial benefits, IIoT implementation faces unique challenges that hold some organizations back, such as legacy systems, costs, data management, and connectivity concerns. How do legacy and outdated systems pose a challenge to the adoption of IIoT in industrial settings, what are the cost-related concerns associated with implementing IIoT, and how can the challenges of IoT data management, encompassing data generation, storage, and integration with various databases, be addressed?
Busting The Automation Myths: 7 Reasons To Embrace Robotics

Despite being the third-largest aerospace manufacturer and having a world-leading premium automotive sector, the UK faces challenges related to labour shortages and low productivity. These issues are intricately linked to the adoption of automation, which is essential for industrial companies to enhance production, quality, and efficiency. While automation has been a proven tool for boosting productivity, the UK lags behind in robot density, ranking 25th globally. How does the UK’s lag in robot density impact its industrial competitiveness, what role does automation play in addressing concerns related to labour shortages, workplace injuries, and staff retention, and how can companies ensure a smooth transition while valuing the expertise of their experienced employees?
UK Officials Use AI To Decide On Issues From Benefits To Marriage Licences

A recent investigation by The Guardian has revealed that government officials in the UK are employing artificial intelligence (AI) and complex algorithms to assist in critical decision-making processes across various sectors, including welfare, immigration, and criminal justice. While AI has been integrated into public service operations, the investigation has raised concerns about the potential for discriminatory outcomes and a lack of transparency in these AI-driven decisions. How has the use of AI and algorithms in government decisions impacted individuals’ lives, especially in areas like welfare, immigration, and criminal justice, what are the key concerns raised by experts and organizations regarding the lack of transparency and accountability in the government’s use of AI for decision-making, and how can these concerns be addressed to ensure fairness and ethics in public services?
Hardware R&D News
Tiny Printed Dynamo Powers Bicycle Inner Tube’s Pressure Sensor
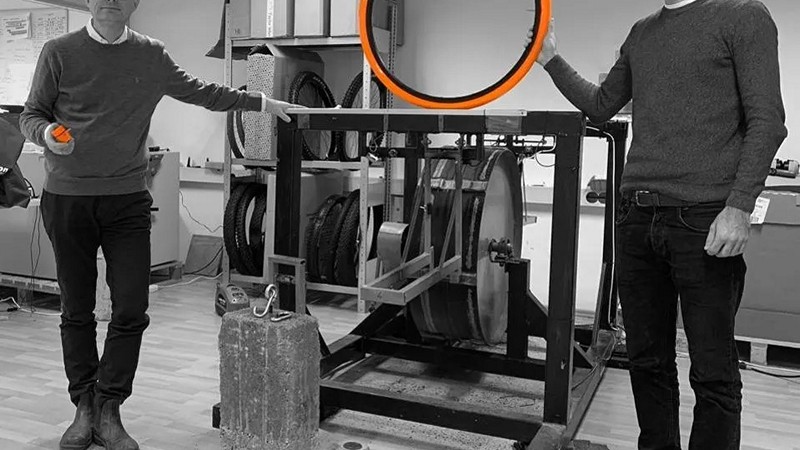

Austrian company Tubolito is pioneering the development of a cutting-edge “nanogenerator” integrated into its distinctive orange bicycle inner tubes to power wireless tire pressure sensors. Unlike conventional battery-powered systems, Tubolito’s technology relies on flexible printed piezoelectric nanogenerators that harvest energy through the tube’s vibration and deformation. This breakthrough innovation enables real-time monitoring of tire pressure, optimizing bicycle performance. What are the key advantages of Tubolito’s nanogenerator-powered tire pressure sensor for cyclists, could Tubolito’s innovation pave the way for similar applications in other industries, beyond cycling, where energy harvesting and real-time monitoring are valuable, and how does the development of energy harvesting technologies like Tubolito’s nanogenerator align with sustainability and environmental goals in the field of sports and outdoor activities?
Wearable Device Makes Memories And Powers Up With The Flex Of A Finger
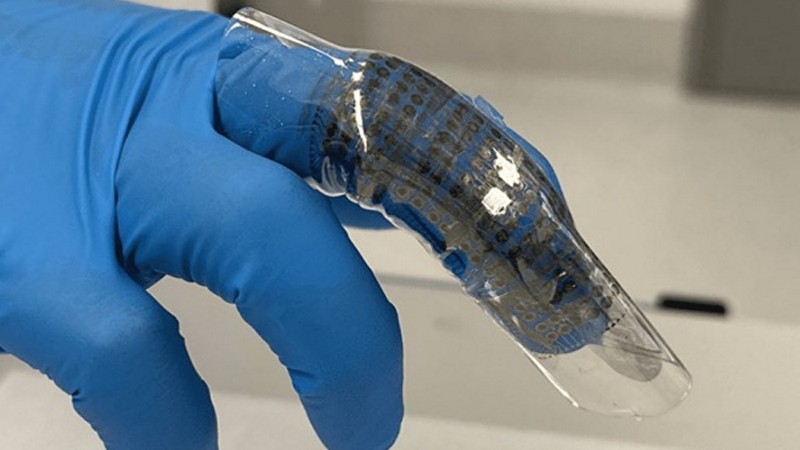
Researchers from RMIT University, in collaboration with the University of Melbourne and other institutions, have developed an experimental wearable device that combines energy generation with memory capabilities. This innovative technology relies on a single nanomaterial encased in a stretchable housing fitted to the user’s finger, allowing power to be generated by simply bending the finger. The multifunctional device represents a significant departure from conventional wearables, as it combines both power generation and memory functions within a super-thin, single-material design. How does the experimental wearable device work in terms of generating power from finger bending, could this innovative technology open the door to more efficient and multifunctional wearables in the future, and what are the challenges and opportunities associated with integrating energy generation and memory capabilities into a single device?
Open-Source Hardware News
What Are RISC-V Chipsets And How Will They Redefine Next-Gen Wearable Tech

The world of computer hardware has long been dominated by architectures such as ARM and x86. These stalwart designs have shaped the CPUs powering some of the most robust and reliable devices on the market. However, a new contender has emerged in the realm of microprocessor architecture: RISC-V chipsets. RISC-V is not just another architecture; it introduces open-source principles that distinguish it from ARM and x86. What are the fundamental differences between RISC-V, ARM, and x86 architectures in terms of open-source principles, what specific advantages does RISC-V offer over its established counterparts, and how could RISC-V influence the development of next-gen wearables?

