Renewable energy sources are often touted as the cost-effective and sustainable future of power generation, and offer energy security, reduce emissions, improve air quality, and stimulate local economies. However, the assertion that renewables are consistently cheaper than fossil fuels may require a closer examination after investors begin pulling out of renewable energy funds. How do the long-term cost calculations for renewable energy sources, like solar panels and wind turbines, compare to those of fossil fuel power stations, how do financial incentives and disincentives affect the true cost of energy generation, and how might interest rates impact the future of renewable energy development?
Top Stories This Week
- Is Renewable Energy Really Cheaper than Fossil Fuels?
- IBM Could Be A Trend-Setter By Offering Customer Protection On Its AI Offerings
- Intel Stock Jumps After Unveiling Plans To Spin-Off Programable Chip Unit
- Bota Systems Raises $2.5m To Help Give Robots Sense Of Touch
- Japan’s Fujitsu, Riken Develop Second Quantum Computer
- You’ve Heard Of Moore’s Law For CPUs, Now Check Out NVIDIA’s Huang’s Law For GPUs
- My Smart Volvo Has Managed To Scrap Itself
- Apple Says Software Bug And Certain Apps Causing iPhone Overheating
- Finger-Shaped Sensor Enables More Dexterous Robots
- New Biosensors Allow Earbuds To Record Brain Activity and Exercise Levels
- Semidynamics And Signatureip Create A Fully Tested RISC-V Multi-Core Environment And CHI Interconnect
Hardware Business News
IBM Could Be A Trend-Setter By Offering Customer Protection On Its AI Offerings

In the fast-paced world of artificial intelligence (AI), where innovation races ahead, concerns regarding AI adoption have been steadily growing. These concerns span a wide spectrum, from questions about the accuracy of AI algorithms to the potential legal risks tied to AI-generated content. Recent legal actions, including lawsuits involving AI language models, have underscored the need for safeguards in the AI landscape. In response to these apprehensions, technology giants IBM and Microsoft have unveiled initiatives designed to address customer fears and catalyse the seamless integration of AI into corporate systems and workflows. What are some of the key concerns and challenges businesses and consumers face when considering the adoption of AI technologies, how have recent legal actions, such as lawsuits related to AI-generated content, added to these concerns, and how does IBM’s indemnification pledge work to alleviate customer fears regarding AI adoption?
Intel Stock Jumps After Unveiling Plans To Spin-Off Programmable Chip Unit

Intel has unveiled its plan to spin off the Programmable Solutions Group (PSG), a division specializing in chips that serve as a link between Intel’s general-purpose semiconductors and binary task-specific chips. This strategic move will result in PSG becoming a standalone business by January, with intentions to go public on a U.S. exchange within the next two to three years. What is the significance of Intel’s decision to spin off the Programmable Solutions Group (PSG), and how does it fit into the company’s broader strategic objectives, what potential advantages and challenges might PSG face as it transitions into a standalone business and prepares for an IPO in the coming years, and how has Intel’s CEO, Pat Gelsinger, approached the restructuring of Intel’s business divisions?
Bota Systems Raises $2.5m To Help Give Robots Sense Of Touch
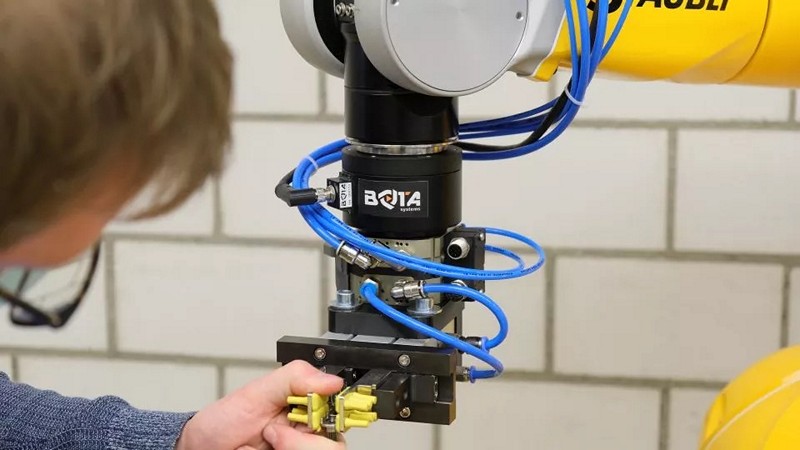

Swiss-based Bota Systems has successfully concluded a $2.5 million seed funding round, led by Marathon Venture Capital and featuring participation from angel investors. Bota Systems specializes in developing force torque sensing solutions that enhance the capabilities of robotic arms by equipping them with the sense of touch. This latest investment will empower Bota Systems to expand its team, meet the rising demand from research institutions and manufacturing companies globally, and further execute its product development roadmap. How does Bota Systems’ force torque sensing technology enhance the capabilities of robotic arms, what potential applications does this enable in industries like manufacturing and research, and how does Bota Systems’ innovation contribute to addressing the limitations often associated with these robots, particularly their lack of a sense of touch?
Japan’s Fujitsu, Riken Develop Second Quantum Computer

In a remarkable stride towards the realization of quantum computing’s transformative potential, Fujitsu and Japan’s state-backed research institute Riken have jointly unveiled Japan’s second quantum computer. Boasting an impressive 64 qubits, this quantum computer is set to play a pivotal role in advancing quantum technology research in Japan and around the world. As part of this innovative initiative, the 64 qubit quantum computer will be integrated with a 40 qubit quantum computer simulator—a tandem effort aimed at surmounting the persistent challenges and errors that have thus far hindered quantum systems from providing precise and reliable results. What are the primary objectives of Fujitsu and Riken in integrating it with a 40 qubit quantum computer simulator, how do these efforts contribute to the advancement of quantum technology research, and how does the collaborative effort between Fujitsu and Riken position Japan in this highly competitive field, especially in comparison to quantum endeavours in China and the United States?
Hardware Engineering News
You’ve Heard Of Moore’s Law For CPUs, Now Check Out NVIDIA’s Huang’s Law For GPUs
In the ever-evolving landscape of the semiconductor industry, the once steadfast Moore’s Law is encountering formidable obstacles. However, as the relentless pursuit of smaller transistors reaches the realm of diminishing returns, an existential crisis looms over the industry. In this climate of uncertainty, NVIDIA, under the visionary leadership of CEO Jensen Huang, has boldly embraced a new era with the advent of “Huang’s Law”. What catalysed the semiconductor industry’s move away from Moore’s Law, how does “Huang’s Law” represent a new era, relying on AI for GPU advancement, and what are the implications of “Huang’s Law” for the semiconductor industry?
My Smart Volvo Has Managed To Scrap Itself

In a world inundated with technological marvels and AI-infused innovations, the modern automobile has not been left untouched by the allure of over-engineering. The pervasive integration of microchips and complex systems into cars has transformed them into sophisticated, interconnected marvels of technology. However, amidst the symphony of sensors, AI-driven safety features, and digital bells and whistles, a counterintuitive question arises: Is there room for a simpler, microchip-free car in our increasingly digital age? How has the integration of microchips and advanced technologies transformed modern automobiles, what are the potential benefits and drawbacks associated with these innovations, and what led to the peculiar incident involving the car’s bonnet and the emergency services call, shedding light on the unintended consequences of over-engineering?
Apple Says Software Bug And Certain Apps Causing iPhone Overheating

In the realm of cutting-edge smartphones, Apple’s iPhone 15 series stands as a paragon of innovation. However, even the paragon occasionally encounters quirks, as users of the iPhone Pro and iPhone Pro Max have recently discovered. Amidst the splendour of its features, these high-end devices have faced a somewhat unexpected challenge: overheating. Apple has diligently undertaken an investigation to unveil the root causes, leaving no stone unturned in identifying the culprits behind the temperature spikes in its flagship phones. What specific factors have been identified by Apple as contributing to the overheating problem in its iPhone 15 Pro and Pro Max models, how critical is the role of third-party apps in this scenario, and how can users ensure that their favourite applications do not contribute to overheating?
Hardware R&D News
Finger-Shaped Sensor Enables More Dexterous Robots
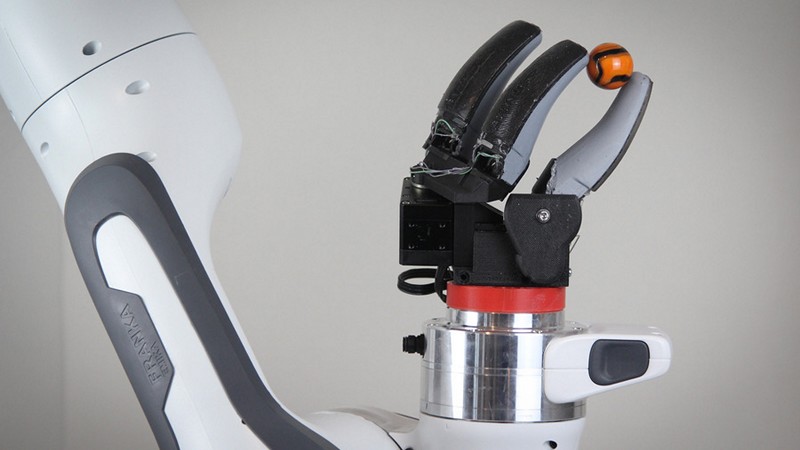

Imagine a robotic hand that can grasp objects not just with its fingertips but with the full length of its fingers, akin to how humans handle diverse objects. MIT engineers have turned this imagination into reality by developing a finger-shaped sensor, the GelSight Svelte, designed to revolutionize how robots perceive and interact with objects. Unlike conventional tactile sensors confined to the fingertips, the GelSight Svelte offers high-resolution tactile sensing across an extended area, fostering versatility in robotic object manipulation. How does the GelSight Svelte sensor differ from traditional tactile sensors in terms of design and functionality, what role do the mirrors and flexible backbone play in its operation, and how might this advancement impact the future capabilities of robots, particularly in tasks that require complex dexterity and tactile sensitivity?
New Biosensors Allow Earbuds To Record Brain Activity and Exercise Levels
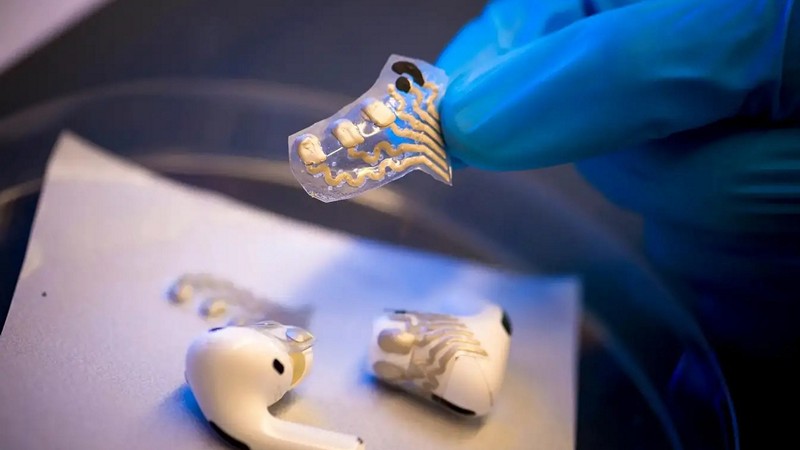
In a ground-breaking development, researchers at the University of California, San Diego, have introduced a transformative capability to commonplace earbuds. These earbuds, when equipped with two flexible sensors, can now capture and record both brain electrical activity and lactate levels in the body. This innovative breakthrough in biosensors allows for seamless health monitoring and early detection of neurodegenerative conditions, expanding the role of everyday audio devices in healthcare. How do the newly introduced sensors enable earbuds to record both brain electrical activity and lactate levels in the body, what are the potential applications of this dual-monitoring capability in healthcare and wellness, and what future therapeutic opportunities might arise from this technology?
Open-Source Hardware News
Semidynamics And Signatureip Create A Fully Tested RISC-V Multi-Core Environment And CHI Interconnect
In the ever-evolving landscape of advanced applications like AI and ML, the demand for powerful chip designs with multiple cores continues to surge. To meet this growing need, Semidynamics and SignatureIP have joined forces, combining their intellectual properties (IPs) to create a fully-tested RISC-V multi-core environment with a Coherent NoC (C-NoC) CHI interconnect. This collaboration promises to facilitate the seamless development of cutting-edge chip designs, revolutionizing the capabilities of RISC-V processors. What specific challenges and demands in AI and ML applications are driving the need for powerful chip designs with multiple core, how does the collaboration between Semidynamics and SignatureIP address these challenges, and how might this impact the broader RISC-V community and the field of semiconductor technology?