In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the advent of quantum computing poses a unique challenge to encryption strategies. The potential of quantum computers to decode encrypted data threatens the very foundation of secure digital communication. However, this challenge also acts as a catalyst for innovation in cryptographic practices. How does the emergence of quantum computing redefine the landscape of cybersecurity, what specific risks does it pose to traditional encryption methods, and as quantum advancements become a reality, how crucial is it for individuals, businesses, and governments to stay informed, agile, and proactive in securing their digital infrastructure?
Top Stories This Week
- Quantum Decryption: Have We Lost the Encryption Battle?
- Silicon Valley Saw OpenAI With Eyes Wide Shut
- New Chinese Chip Uses IBM’s Open Standard Power ISA Instead Of X86 Or ARM
- UK Investors Back Startup Making EV Motors Without Rare Earths
- IBM To Invest In New AI Skills Training Programme To Boost Global Workforce
- The History Of The Microchip: How A Tiny Device Changed the World
- Why Apple Is Working Hard To Break Into Its Own iPhones
- Robotic Excavator Builds A Giant Stone Wall With No Human Assistance
- Researchers Create Ingestible Sensor That Monitors Heart Rate From the Gut
- A Brain-Monitoring Device May One Day Take The Guesswork Out Of Anaesthesia
- RISC-V: How Companies Are Pushing It Into The Future
Hardware Business News
Silicon Valley Saw OpenAI With Eyes Wide Shut

The recent upheaval at OpenAI, a prominent player in artificial intelligence (AI), reflects the tumultuous nature of the technology it champions. Following the dismissal of CEO Sam Altman and Chairman Greg Brockman by four directors, reports suggest Altman may stage a return. However, the incident exposes underlying issues: the unproven nature of AI technology, governance challenges, and a valuation that raises eyebrows. As the saga unfolds, troubling realities persist, prompting a closer examination of OpenAI’s trajectory. Amid the leadership shakeup, how might the governance structure of OpenAI, initially conceived as a non-profit entity for societal benefit, contribute to conflicted interests and impact the company’s future direction, with concerns about the quality decline in OpenAI’s GPT-4 model, what implications does this have for the broader landscape of AI technology, and how might it affect OpenAI’s standing as a leader in the field?
New Chinese Chip Uses IBM’s Open Standard Power ISA Instead Of X86 Or ARM

Hexin Technology, a Chinese CPU developer, has achieved a significant milestone with the successful powering-on of its second-generation test chip, the HX-C2000 TC2. Positioned as a key player in China’s quest for CPU autonomy amidst U.S. sanctions, Hexin’s HX-C2000 boasts 110 billion transistors and utilizes IBM’s open standard Power ISA. The company aims to deploy this processor across diverse applications, including artificial intelligence (AI), big data, and cloud computing. How does Hexin Technology’s adoption of IBM’s Power ISA impact the landscape of server CPUs, what advantages or challenges might arise from this departure from more commonly used instruction set architectures, and how does Hexin’s progress with the HX-C2000 TC2 contribute to the nation’s efforts to establish self-reliance in CPU and GPU technologies?
UK Investors Back Startup Making EV Motors Without Rare Earths
UK-based startup Advanced Electric Machines (AEM) has secured $29 million in Series A funding, propelling its mission to redefine electric vehicle (EV) motors without relying on rare earths or copper. This breakthrough not only makes AEM’s motors 100 percent recyclable but also introduces a game-changing approach to manufacturing. With ambitious plans to scale up production, AEM envisions crafting EV motors that enhance vehicle range by at least 10 percent. How does AEM’s innovative approach of developing EV motors without rare earths or copper mark a significant departure from conventional motor manufacturing, what implications does this have for the broader electric vehicle industry, and how does AEM’s technology align with the strategic goals of automakers in Europe, the US, and Japan?
IBM To Invest In New AI Skills Training Programme To Boost Global Workforce

IBM is embarking on a groundbreaking venture to address the widening skills gap in artificial intelligence through a new training program. Over the next three years, the initiative aims to reach 2 million learners globally, prioritizing underrepresented communities. Building on the foundation of its IBM SkillsBuild platform, this collaboration with non-governmental organizations and partners worldwide will provide free access to AI education. How does IBM’s global initiative to train 2 million learners in AI contribute to closing the skills gap, especially in underrepresented communities, what potential impact might this have on the broader landscape of AI-driven innovation, and as AI becomes increasingly integral to various industries, how does IBM plan to ensure inclusivity in its training program, particularly targeting diverse learners and addressing the evolving demands of the AI job market?
Hardware Engineering News
The History Of The Microchip: How A Tiny Device Changed the World
The microchip, a marvel often smaller than a fingernail, has become the linchpin of the digital era, powering devices from basic gadgets to advanced supercomputers. Its evolution from a conceptual idea to a vital element in nearly all modern technology is a captivating narrative of innovation, deception, and global influence. How has the history of the microchip reflected the intersection of curiosity, creativity, and perseverance, how have these qualities shaped the trajectory of technological progress in the digital age, and how challenges in electronics drive the need for a new approach in electronics design, ultimately leading to the development of integrated circuits?
Why Apple Is Working Hard To Break Into Its Own iPhones
In the realm of personal technology, where iPhones have become indispensable extensions of our lives, Apple has quietly elevated its defence mechanisms against unseen threats. Beyond the glossy screens and sleek designs, a covert battle unfolds in the heart of Paris, where Apple engineers rigorously test and fortify their devices against cyber adversaries. How do Apple’s Parisian labs employ cutting-edge hardware techniques to anticipate and thwart potential security breaches before iPhones hit the market, in the face of escalating cyber threats, what role does Lockdown Mode play as a safeguard, and as Apple invests significant resources in staying ahead of cyber threats, how does the company navigate the geopolitical complexities and potential clashes with governments while upholding its commitment to user security and privacy?
Robotic Excavator Builds A Giant Stone Wall With No Human Assistance
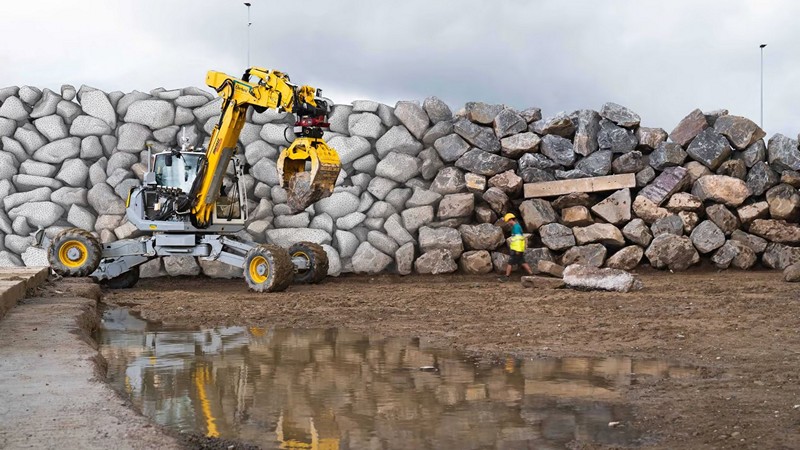

In the realm of construction, where precision meets the formidable challenge of stacking irregular boulders to create stable structures, a remarkable innovation has emerged. Meet HEAP (Hydraulic Excavator for an Autonomous Purpose), a transformed 12-ton Menzi Muck M545 walking excavator, created by the pioneering minds at the ETH Zurich research institute. HEAP’s recent feat involves autonomously scanning and mapping a construction site, lifting massive boulders, and employing machine vision to craft a substantial 20-ft high, 213-ft long dry-stone wall. How does HEAP utilize GNSS, LiDAR sensors, and machine vision technology to autonomously scan a construction site, assess boulders, and strategically build a dry-stone wall, in what ways does HEAP’s ability to use locally sourced boulders enhance sustainability and reduce energy consumption in the construction process, and what potential applications and advancements can we envision for this technology in the broader field of civil engineering and infrastructure development?
Hardware R&D News
Researchers Create Ingestible Sensor That Monitors Heart Rate From the Gut
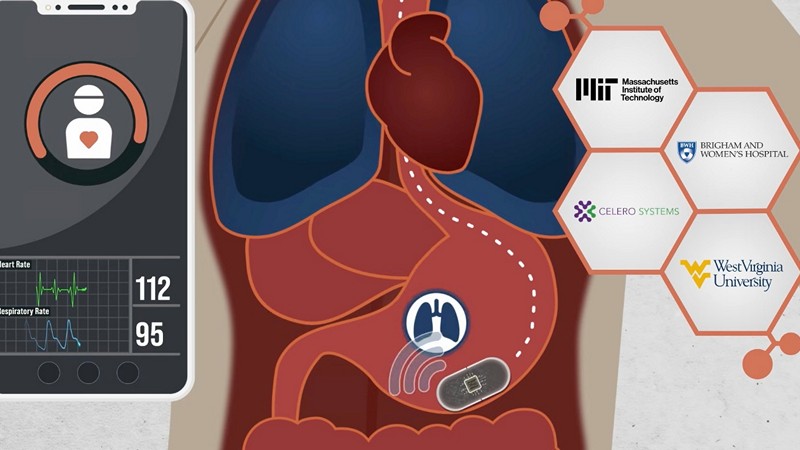
In a ground-breaking development, researchers at MIT have introduced an ingestible capsule, comparable in size to a multivitamin, designed to revolutionize the monitoring of vital signs from within the gastrointestinal tract. The capsule, equipped with an accelerometer, aims to diagnose sleep apnoea without the need for cumbersome sensors. However, its potential reaches beyond, as it could play a crucial role in detecting opioid overdoses in high-risk patients. How does the accelerometer-equipped ingestible capsule precisely measure vital signs, particularly breathing and heart rate, within the gastrointestinal tract, in what ways can this innovative capsule contribute to the early detection of conditions such as opioid overdoses, asthma, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and what are the challenges in extending its monitoring duration beyond a day or two?
A Brain-Monitoring Device May One Day Take The Guesswork Out Of Anaesthesia
In a leap toward achieving precision in anesthesia delivery, a new brain-monitoring device emerges as a potential game-changer. Developed to be the Goldilocks of anesthesia, this automated system, tested on rhesus macaques, adjusts drug doses every 20 seconds based on monitored brain activity. The goal is to administer just the right amount of anesthetic, avoiding the risks associated with excess dosage. How does the brain-monitoring device, equipped with algorithms, calculate and adjust anesthetic doses in real-time based on monitored brain activity, how does this automated system address the limitations of current approaches, particularly in minimizing the risks associated with excessive sedation, and what are the key considerations and challenges in transitioning this technology for human use?
Open-Source Hardware News
RISC-V: How Companies Are Pushing It Into The Future

RISC-V, the rising star in the world of instruction set architectures (ISA), is gaining unprecedented traction, challenging the long-standing dominance of x86 and ARM. Big players like Qualcomm, Google, Intel, and Red Hat are rallying behind RISC-V, signalling a potential shift in the tech landscape. How does RISC-V differ from traditional instruction set architectures like x86 and ARM, what advantages or challenges does its open-source, royalty-free model present in the realm of CPU architecture, and while RISC-V has made inroads, particularly in China and Russia, how does its current status compare to established ISAs like ARM, and what are the strategic considerations for major players like Intel in investing heavily in RISC-V despite ARM’s existing market dominance?

