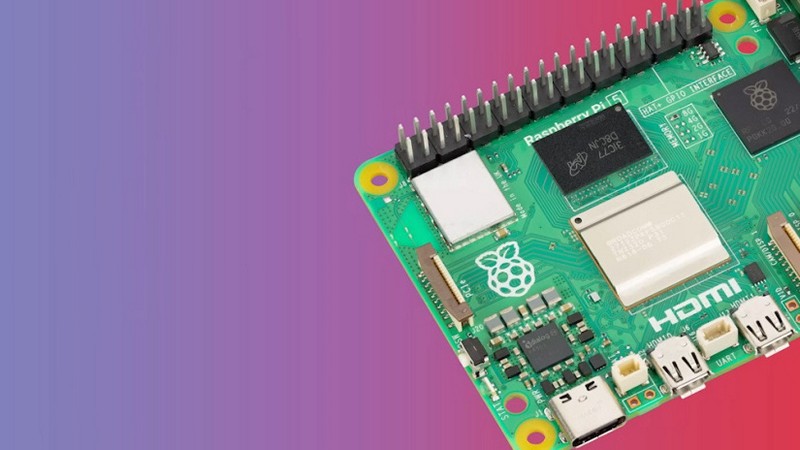
In an unexpected turn of events, the Raspberry Pi Foundation, known for its pioneering single-board computers (SBCs), has unveiled the Raspberry Pi 5, defying expectations that the Raspberry Pi 4 would be the final iteration. This surprising release comes as the Foundation addresses challenges it has encountered in recent years. The Raspberry Pi 5 introduces custom silicon solutions that promise to revolutionize the world of SBCs. What challenges has the Raspberry Pi Foundation faced in recent years that led to the development of the Raspberry Pi 5, how has the Foundation’s experience with supply shortages and dependencies on chip manufacturers influenced its decision to create custom silicon solutions, and what are the key features and specifications of the Raspberry Pi 5, including the custom silicon components like the RP1 I/O chip?
Top Stories This Week
- Raspberry Pi 5 Just Announced – Major Upgrades Ahead!
- China To Build Huge Particle Accelerator For Lithography
- Huawei’s Defiance: Mate 60 Pro Reveals Tech Trade War Loopholes
- Teslabot Shows Off New Skills In Latest Video
- Getty Made An AI Generator That Only Trained On Its Licensed Images
- Robots on Patrol: The Future of Crime Prevention
- Starpath Robotics Wants To Mine Moon Water For Rocket Fuel For Off-World Colonies
- What If IBM Z Could Help Stop Fraud?
- New Wearable Sensor Makes Continuous Analysis Of Sweat Possible
- These Robotic Acoustic Swarms That Can Mute Different Areas Of A Room
- Rivos, A RISC V Startup Countersues Apple, Claiming That Apple Intimidates Workers Who ‘Dare To Leave’
Hardware Business News
China To Build Huge Particle Accelerator For Lithography
A ground-breaking initiative is underway to construct a particle accelerator with a circumference ranging from 100 to 150 meters (328 to 492 feet) in China. This accelerator aims to serve as a central hub for multiple lithography machines so that China can continue to develop semiconductors past the 7nm barrier. Significant progress has already been made in such devices, with Tsinghua University successfully constructing an SSMB prototype last year, and the prototype’s designed EUV power exceeded 1kW. What challenges has China faced with access to lithography machines, how might this innovation transform the field of lithography and related industries, and what advantages does SSMB offer, particularly in terms of continuous light production and average power?
Huawei’s Defiance: Mate 60 Pro Reveals Tech Trade War Loopholes
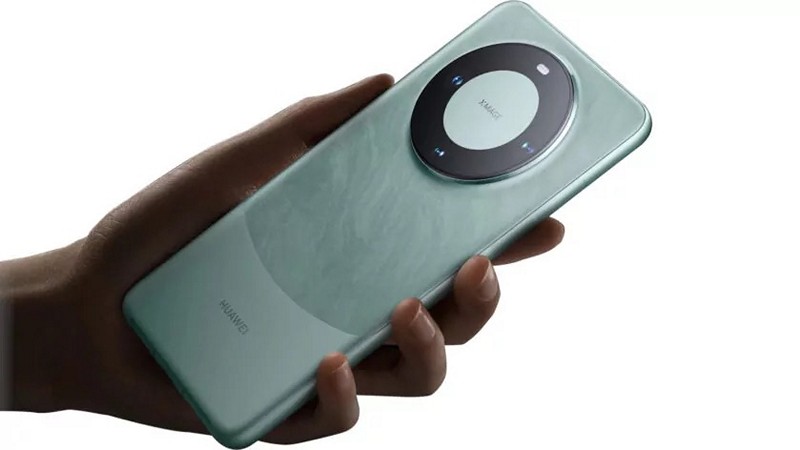

In the ever-evolving saga of global tech conflicts, a recent exploration into the innards of the Huawei Mate 60 Pro has unearthed astonishing revelations. As the United States persists in its quest to curb China’s access to critical technologies, the latest iteration of Huawei’s flagship device surprisingly boasts 7nm components, but more astonishingly, integrates South Korean RAM modules—a feat that should have been beyond China’s reach. This discovery rekindles the debate surrounding Western sanctions on semiconductor trade and their consequences. What were the initial objectives behind Western sanctions against China, how have these measures evolved over time, and what recent developments indicate that China is resilient and resourceful in navigating these restrictions?
Teslabot Shows Off New Skills In Latest Video
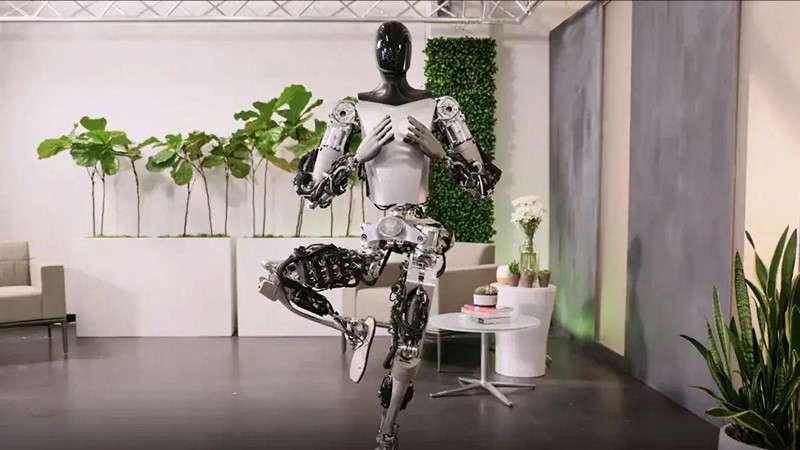

Tesla’s Optimus, the highly anticipated humanoid robot, is making significant strides in its development, as revealed in a recent video posted by the official Tesla Optimus account. The video showcases Optimus operating on the same end-to-end neural network used by Tesla’s cars, enabling it to process video input and generate precise control outputs. Additionally, the robot was also shown to be able to handle objects with a great degree of dexterity, even accounting for mistakes. Despite these advancements, the project remains in development and actively seeks additional engineering talent. What changes have the engineering team at Tesla made to their Optimus robot, what challenges does the robot continue to face, and how far away is it to becoming a practical reality?
Getty Made An AI Generator That Only Trained On Its Licensed Images

Getty Images has teamed up with Nvidia to introduce “Generative AI by Getty Images,” a ground-breaking tool that enables users to create images using Getty’s extensive library of licensed photos. This collaboration leverages Nvidia’s Edify model, available in its generative AI model library Picasso, to provide users with powerful image generation capabilities. Notably, this tool grants full copyright indemnification to users, ensuring legal protection when publishing images created with it for commercial use. How does the integration of Getty Images’ vast library of licensed photos with Nvidia’s generative AI technology benefit users, what sets “Generative AI by Getty Images” apart from other AI-driven image generation tools in terms of copyright indemnification, and how does Getty Images manage content restrictions?
Hardware Engineering News
Robots on Patrol: The Future of Crime Prevention

The evolving landscape of modern policing faces an array of challenges, from resource constraints and changing technologies to the need for proactive crime prevention. As law enforcement grapples with these complexities, the prospect of deploying police robots has emerged as a potential solution. What are the primary challenges faced by modern policing, particularly in the context of resource limitations and shifts from proactive to reactive approaches, how do these challenges impact public safety and law enforcement’s effectiveness, and while the potential benefits of police robots are evident, what ethical concerns and privacy issues could arise from their widespread deployment?
Starpath Robotics Wants To Mine Moon Water For Rocket Fuel For Off-World Colonies
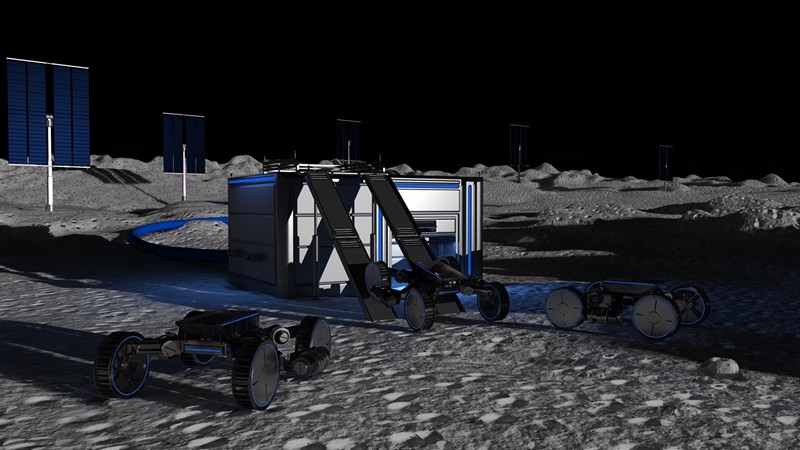
Starpath Robotics has emerged from stealth with an audacious plan to leverage advanced machines for mining and refining water on the moon and Mars. Their goal is to produce rocket propellant using local resources, a concept known as in-situ resource utilization (ISRU). This ambitious endeavour not only holds the promise of enabling self-sustaining human colonies in space but also has garnered significant attention from investors. How does Starpath Robotics plan to overcome the formidable challenges posed by the lunar South Pole’s extreme conditions, such as near-permanent darkness and sub-zero temperatures, to ensure the successful deployment and operation of mining machines, what innovative technologies are they developing to thrive in these harsh environments, and what role does SpaceX’s Starship play in their long-term plans?
What If IBM Z Could Help Stop Fraud?

IBM is pioneering the infusion of AI capabilities into its mainframe systems, particularly the IBM z16, to unlock new levels of efficiency, security, and competitiveness. By integrating AI into transaction processing and mission-critical workloads, IBM aims to provide its customers, including major banks and insurance companies, with low-latency AI processing that can transform industries dependent on mainframe computing. How does the integration of AI, specifically AI inference processing, on the IBM z16 enhance the capabilities of mainframe computing for applications like credit card fraud detection, what unique advantages does low-latency AI processing bring to institutions running mission-critical workloads on IBM Z systems, and how does the new toolkit empower clients to deploy open-source AI confidently in production environments on IBM Z systems?
Hardware R&D News
New Wearable Sensor Makes Continuous Analysis Of Sweat Possible
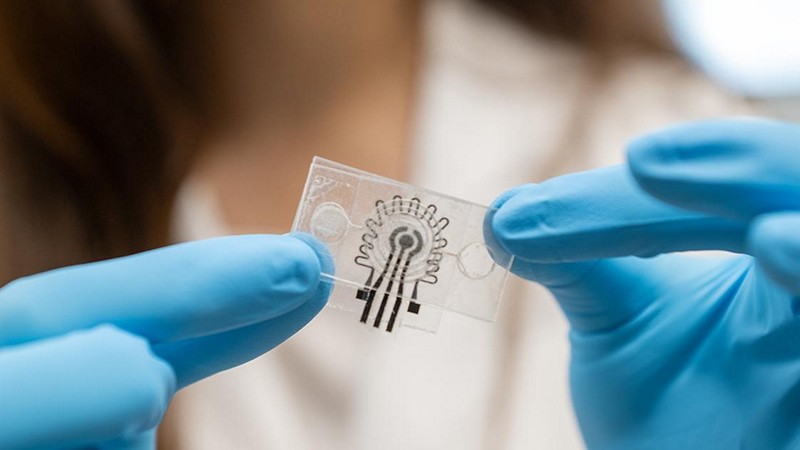

Researchers at Penn State have developed a ground-breaking wearable patch capable of continuous monitoring of glucose levels in sweat, offering potential insights into human health. Unlike previous wearable sensors, this laser-modified graphene nanocomposite patch boasts the durability and specificity required for extended monitoring, lasting up to three weeks while concurrently measuring body temperature and pH levels. The team believes that this innovation could have significant implications for personalized medicine, population health, and precision nutrition. What distinguishes this novel wearable patch from previous sweat biosensors, how does it overcome the challenges related to low biomarker concentration levels, variability in pH, salinity, and temperature, and how does the device account for these fluctuations and maintain accurate glucose measurements during activities like exercise and eating?
These Robotic Acoustic Swarms That Can Mute Different Areas Of A Room
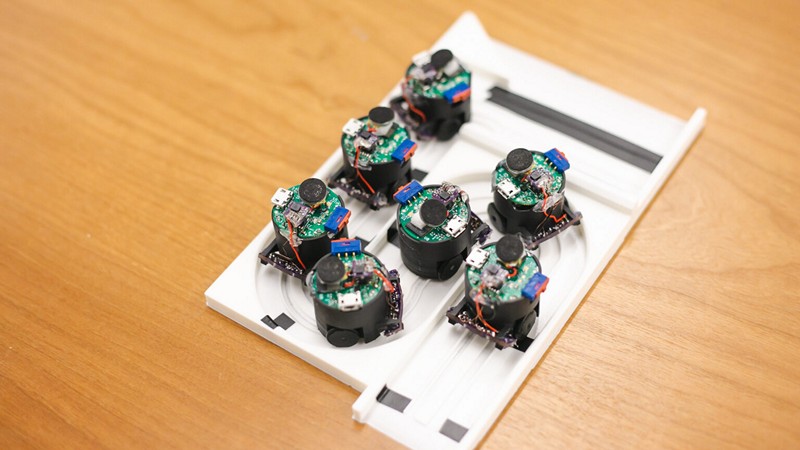

A team of researchers from the University of Washington has unveiled an innovative development in robotics: shape-changing smart speakers capable of autonomously creating speech zones within rooms and tracking individual speakers’ positions. Powered by deep learning algorithms, these miniature robots, each around one inch in diameter, can separate simultaneous conversations and mute specific areas, even when dealing with individuals possessing similar voices. Unlike previous robot swarm projects, this system relies solely on sound, eliminating the need for overhead cameras, projectors, or specialized surfaces. How do the shape-changing smart speakers use deep learning algorithms to distinguish between voices and accurately create speech zones within a room, what challenges did the researchers face in ensuring precise sound control and zone separation, and what potential applications do they envision for this technology in smart homes and other settings?
Open-Source Hardware News
Rivos, A RISC V Startup Countersues Apple, Claiming That Apple Intimidates Workers Who ‘Dare To Leave’

Rivos, a RISC-V startup, has launched a countersuit against tech giant Apple, alleging that Apple employs tactics to intimidate and restrict employees who leave the company to work elsewhere. The countersuit, filed by Rivos and six former Apple employees, intensifies an ongoing trade secrets dispute initiated by Apple last year, accusing Rivos and former Apple staff of sharing sensitive chip technology. Rivos now seeks to have Apple’s “overbroad” non-disclosure and non-solicit agreements deemed unenforceable, claiming that Apple employs anti-competitive practices to deter competition and stifle emerging startups. What specific allegations does Rivos make in its countersuit against Apple regarding the tech giant’s treatment of employees who leave to work for other companies, how does Rivos argue that Apple’s practices harm competition and emerging startups, and how does Rivos plan to defend against these accusations and establish that Apple’s restrictive agreements are unenforceable?
