The ongoing debate about artificial intelligence (A.I.) is centred around the question of what the technology can do, but the more important question is how it will be used, and by whom. The fear of A.I. is mostly about how capitalism and governments will use the technology against individuals, however, in a recent interview with Margaret Mitchell, the chief ethics scientist at A.I. firm Hugging Face, it was suggested that these systems are poorly suited to be integrated into search engines as they are not trained to predict facts, but to make up things that look like facts. This article raises questions about the business models that will power A.I., who these machines will ultimately serve, and whether they will be aligned with the interests of their users, or of the corporations and governments that control them.
Top Stories This Week
- The Imminent Danger Of AI No One Is Talking About
- Elon Musk’s False Promises: Shareholders Sue Tesla CEO Over Autopilot Claims
- Tiktok Answers Three Big Cyber-Security Fears About The App
- How Microchips Migrate From China To Russia
- PLCnext Community Gets Beehind Next-gen Smart Hive Technology
- Tesla Is Going (Back) To EV Motors With No Rare Earth Elements
- How The Design Of Autonomous Weapons Is Changing The Rules Of War
- Next-Generation Sweat Sensor Could Detect Health-Relevant Biomarkers
- Team Creates New Lidar System That Could Improve Autonomous Driving Safety
- Makers Making Change Helps People With Disabilities Using 3D Printing Technology
Hardware Business News
Elon Musk’s False Promises: Shareholders Sue Tesla CEO Over Autopilot Claims

Recently, Tesla CEO Elon Musk has been slapped with another lawsuit from shareholders, claiming that promises surrounding Autopilot were false, resulting in a fall in share price. The lawsuit comes after a series of failed attempts to deliver on Musk’s self-driving promises, which have caused stock prices to fluctuate. Despite setbacks with Tesla, Musk continues to innovate in other areas, such as SpaceX’s rocket launches and EV development, but the recent lawsuit raises questions about the future of his leadership. Why is self-driving such a complex problem to solve, what does the lawsuit mean for Elon Musk, and could this be the start of the end for Elon Musk and his false promises?
Tiktok Answers Three Big Cyber-Security Fears About The App

The fate of TikTok seems to be hanging in the balance as governments in different countries, including the US, Canada and the EU, have raised concerns over the cybersecurity risks posed by the social media app. TikTok, a Chinese-owned company, has been accused of collecting excessive amounts of data, spying for the Chinese government, and even acting as a tool for brainwashing. TikTok executives have repeatedly tried to assure people that the Chinese staff can’t access the data of non-Chinese users, but ByteDance, the owner of TikTok, admitted that several of its Beijing-based employees accessed the data of at least two US journalists and a “small number” of others to track their locations and check whether they were meeting TikTok employees suspected of leaking information to the media. In this article, the BBC explores the three main cybersecurity concerns regarding TikTok and how the company responded to them.
How Microchips Migrate From China To Russia

Despite the West threatening sanctions on anyone selling microchips to Russia, recent leaks and publicly available data reveal that chips keep showing up on Russian shores, with China at the centre of the trade. The adaptability of global trade networks in response to sanctions and tariffs isn’t a new story, but stemming the flow of semiconductors into Russia presents a particularly tough problem as China sits at the centre of the global chip trade. As Western nations are discovering, trying to stifle trade flows of more commoditised items like basic semiconductors is a different matter. Can the US curb the flow of semiconductors to Russia, how will China’s refusal to join Western sanctions on Russia affect trade, and what can be done to prevent Chinese goods from making their way to third-party countries?
Hardware Engineering News
PLCnext Community Gets Beehind Next-gen Smart Hive Technology

The Beehyve project from the PLCnext Community is on a mission to create smart hives that promote bee health and care through the use of swarm intelligence from challenge participants. With the overarching goal of creating an intelligent home for bees that can improve bee health, optimise the hive, and provide an automated hive system to support beekeeper activities, the project is inviting bee enthusiasts with diverse expertise to help construct an automated smart hive. But how does the PLCnext Technology ecosystem help achieve this goal, what is the significance of a smart beehive in the beekeeping industry, and how will the use of LoRaWAN technology benefit beekeepers in real-time?
Tesla Is Going (Back) To EV Motors With No Rare Earth Elements

Tesla announced at its Investor Day that it would develop a new permanent magnet electric vehicle motor without any rare earth elements, which is significant as rare earth elements are often hard to secure and are mainly sourced or processed in China. Rare earth elements are mainly used in electric car motors, with Neodymium being the most commonly used in powerful magnets, and Tesla has previously reduced rare earth usage in its Model 3 drive units by 25%. While it is unclear which material Tesla plans to use as a replacement, it seems to be close to a decision. This article explores the questions about the future of rare earth elements in EV supply chains, the potential impact on the environment, and whether other automakers will follow suit.
How The Design Of Autonomous Weapons Is Changing The Rules Of War
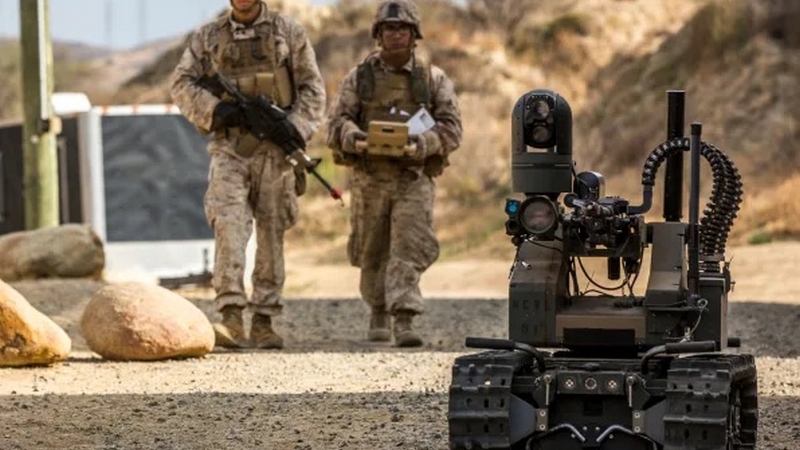

Recent military operations in Ukraine and Nagorno-Karabakh have underlined the value of weaponised artificial intelligence, leading to increased pressure to deploy fully autonomous weapons, which do not require any human supervision. Critics, however, argue that autonomous weapons lack the necessary human judgment to distinguish between civilians and legitimate military targets and warn of the risk of destabilising arms races. In response to the changing nature of war, the U.S. military has issued an update to its Department of Defense directive, indicating an increased commitment to the development and use of autonomous weapons, with the goal of achieving decisive battlefield advantages. The updated directive promises the ethical use of autonomous weapons, but critics argue that it fails to establish guidelines for appropriate levels of human judgment. What potential risks could arise from the development and use of fully autonomous weapons in warfare, how can ethical use of autonomous weapons be ensured, and how might the proliferation of autonomous weapons systems affect the balance of power among nations and lead to arms races?
Hardware R&D News
Next-Generation Sweat Sensor Could Detect Health-Relevant Biomarkers
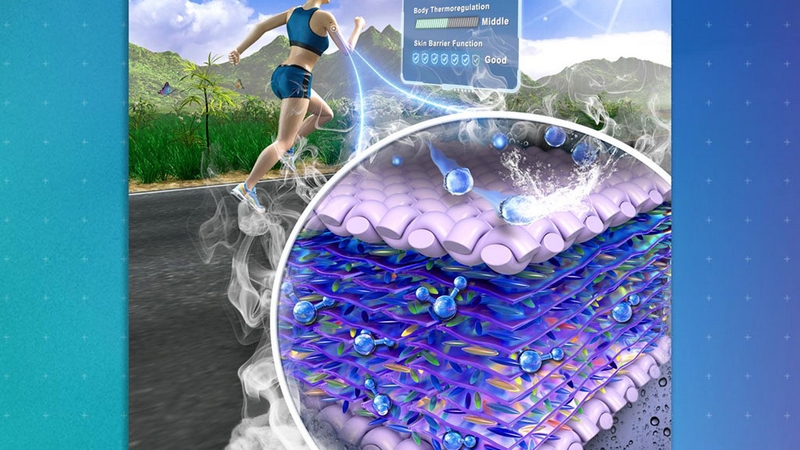

Wearable sensors have revolutionised the field of healthcare, allowing doctors to monitor and diagnose health conditions in real-time, with one such breakthrough technology being the use of biomarkers in sweat, which provides valuable insights into a person’s health. However, current sensors can only measure liquid sweat and not insensible perspiration, which is secreted slowly. To address this issue, researchers at Penn State have developed a superhydrophobic biosensor that can measure sweat vapour, which could act as a diagnostic tool to detect health problems and provide a low-cost device platform for smart healthcare and personalised medicine. What are the benefits of using sweat as a diagnostic tool, how does the superhydrophobic biosensor work, and what are the future implications of this technology for healthcare and personalised medicine?
Team Creates New Lidar System That Could Improve Autonomous Driving Safety

Scientists from Kyoto University in Japan have recently developed a new 3D lidar system that can measure the distance of poorly reflective objects, track their motion, and fit in the palm of a hand. Using a unique chip-based light source called a dually modulated photonic-crystal laser (DM-PCSEL), the system combines flash and scanning illumination, and does not require bulky external optical elements or moving parts, making it more reliable, inexpensive and compact than most current lidar systems. The team believe the system could be used to make autonomous driving safer by allowing robots and vehicles to navigate dynamic environments without losing sight of poorly reflective objects. What is the technology behind this new lidar system, what are the advantages of using a non-mechanical lidar system, and how could this new system be used in autonomous driving and robotics?
Open-Source Hardware News
Makers Making Change Helps People With Disabilities Using 3D Printing Technology
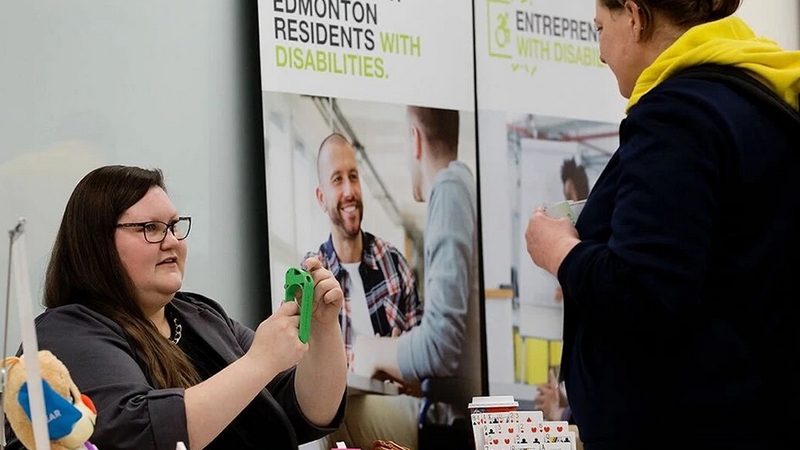

Makers Making Change, a not-for-profit organisation, is helping people with disabilities in Canada and the United States by connecting them with volunteer makers to build assistive technology using 3D printing at an affordable price. According to Statistics Canada, over 80% of people with disabilities reported using at least one assistive device, with cost being the most common reason for unmet needs. Makers Making Change’s open-source platform allows individuals with disabilities to browse devices online, download and 3D print them, or connect with a volunteer who can do it for them. In this article, explore how this organisation is making a positive impact on the lives of people with disabilities, how are volunteers and staff developing cost-effective assistive devices, and how can people can get involved.