The Open Source Hardware Association Summit 2023 has been officially announced, with the event taking place at NYU, New York, on April 28th and 29th. Tickets can now be purchased via the official OSHWA site, and the entire event will be live-streamed over YouTube for those who cannot attend in person. Ponoko firmly believes in the importance of open-source hardware, and fully supports the OSHWA movement to provide hardware to all without restriction.
Top Stories This Week
- Open Source Hardware Association Summit 2023
- Swap’s Robotic Mowers Score $7M In Seed Funding
- Qualcomm Wants To Solve IoT Challenges With Aware Platform
- Microsoft Researchers Are Using Chatgpt To Instruct Robots And Drones
- BlueSleuth-Lite: The Active Surveillance Device For Apple AirTags
- 14 Essential Steps To Take To Secure Household IoT Devices
- First Wearable Device For Vocal Fatigue Senses When Your Voice Needs A Break
- Certain Wearable Gadgets Could Pose Serious Risks To Implantable Electronic Devices
- This Bionic Finger Uses Touch To “See” Inside Human Tissue
- Custom, 3D-Printed Heart Replicas Look And Pump Just Like The Real Thing
- 3d Printing Antennas With Dielectric Resin
Hardware Business News
Swap’s Robotic Mowers Score $7M In Seed Funding
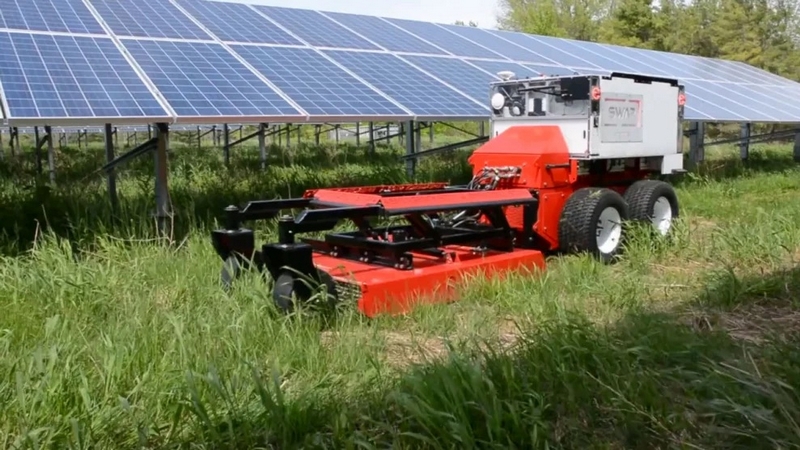

As the world becomes increasingly aware of the environmental impact of traditional energy sources, the demand for clean and renewable energy is on the rise. This shift towards sustainability has given birth to a new industry focused on solar energy, but maintaining solar farms can be costly and time-consuming, which is why Swap Robotics has found success in the industry with its modular robots designed for solar vegetation-cutting. But what sets Swap apart from other robotics companies, how has it managed to secure $7 million in funding during a challenging economic climate, and what does the future hold for the company and the solar industry?
Qualcomm Wants To Solve IoT Challenges With Aware Platform

Qualcomm, a leader in mobile and wireless technology, aims to tackle the fragmentation issues that have plagued the Internet of Things (IoT) space with its new platform, Aware. By combining its silicon with a cloud framework and featuring developer-friendly tools such as open APIs, Qualcomm hopes to make it easy for enterprises to create customised IoT solutions. Can Qualcomm’s Aware platform revolutionise the IoT space and become a game-changer, what vertical markets will Qualcomm target with Aware, and will it be able to foster a much larger IoT market than what exists today?
Microsoft Researchers Are Using ChatGPT To Instruct Robots And Drones
The capabilities of artificial intelligence are continuously expanding, and OpenAI’s ChatGPT is no exception. This language model can not only generate coherent text responses to natural language prompts, but it can also be used to instruct robots without requiring a background in programming or robotics. Microsoft recently conducted research to explore ChatGPT’s potential in the physical world, focusing on robotics tasks, with the research generating fascinating results, including ChatGPT’s ability to use sensor feedback to write code for robot actions. But how does ChatGPT solve problems while considering the laws of physics and the context of the environment, can ChatGPT help protect AI from hackers, and how will ChatGPT’s capabilities impact the future of robotics and human-to-robot interactions?
BlueSleuth-Lite: The Active Surveillance Device For Apple AirTags
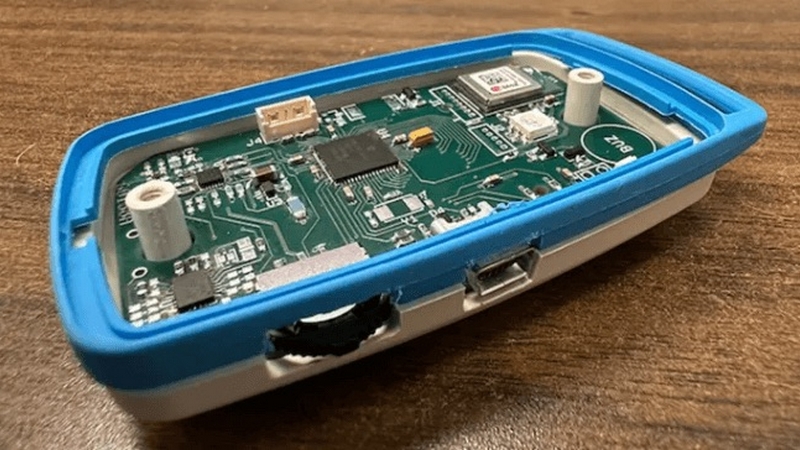

A new crowdsourced project is being developed to fight against the misuse of Apple AirTags, which use Bluetooth, UWB and GPS technology to track the location of personal devices. While AirTags are designed to help users track their personal belongings, they can also be misused for stalking and other crimes, posing a danger to personal safety and privacy. The project aims to detect and track the use of AirTags in a mesh network to prevent such misuse, highlighting the growing need for active personal surveillance and location detection to ensure the safety and privacy of individuals. What challenges has the Apple AirTag introduced, what does the new device propose to do, and could this be the first step in active personal surveillance?
Hardware Engineering News
14 Essential Steps To Take To Secure Household IoT Devices

The Internet of Things (IoT) has become a part of our daily lives, with smart devices ranging from refrigerators to personal assistants, but these days, consumers may be more focused on the benefits of these devices than on their security. IoT devices are just as vulnerable as any other internet-connected hardware, and their data exchanges make them a target for hackers. In this Forbes article, 14 members of the Forbes Technology Council share their opinions on essential cybersecurity steps consumers should take to protect their IoT devices.
First Wearable Device For Vocal Fatigue Senses When Your Voice Needs A Break

Recently, Northwestern University scientists have developed a smart wearable device that continuously tracks vocal use and alerts users to potential overuse, vocal fatigue and potential injury. The device has the potential to help a wide range of people who use their voices for a living, including professional singers, teachers, politicians, and coaches, and even has potential medical uses to monitor patients with voice disorders remotely. How will this device impact the professional singing industry, will this device be useful for non-professional users, and how will it change clinical monitoring of voice disorders?
Certain Wearable Gadgets Could Pose Serious Risks To Implantable Electronic Devices
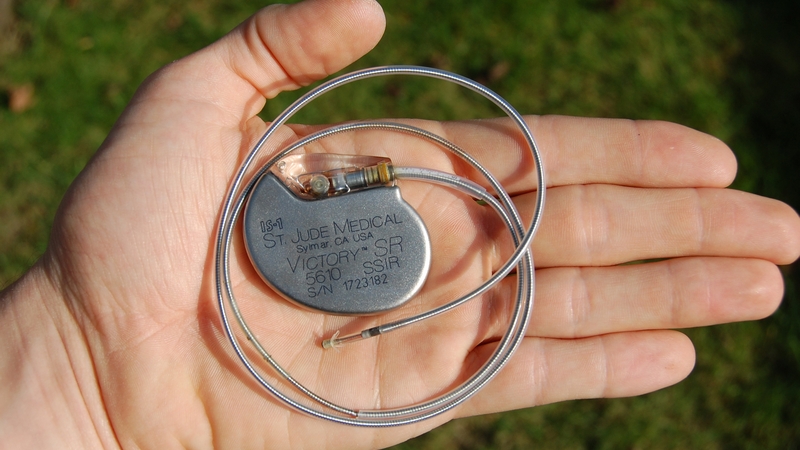

Wearable fitness and wellness trackers have become increasingly popular in recent years, allowing people to monitor their health and fitness in real-time. However, a new study published in Heart Rhythm suggests that specific trackers could pose serious risks for people with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs), such as pacemakers and implantable cardioverter defibrillators. What are the potential risks of wearing a fitness tracker if you have a CIED, how can individuals with CIEDs ensure that the devices they wear are safe, and what steps can be taken to ensure wearables are properly evaluated for safety?
Hardware R&D News
This Bionic Finger Uses Touch To “See” Inside Human Tissue
The human fingertip is an incredible instrument capable of perceiving objects in our environment through the sense of touch. However, until now, artificial tactile sensors have been limited in their ability to recognise and discriminate between external shapes, surface textures, and hardness, without the ability to sense subsurface information. In a recent paper published in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science, a team of Chinese scientists mimicked the underlying perceptual mechanism of the human finger to create a bionic finger with an integrated tactile feedback system capable of detecting and mapping out details below the surface layer of complex objects. What makes this bionic finger so unique, how does it work, and could this lead to further advancements in non-destructive testing technologies?
Custom, 3D-Printed Heart Replicas Look And Pump Just Like The Real Thing
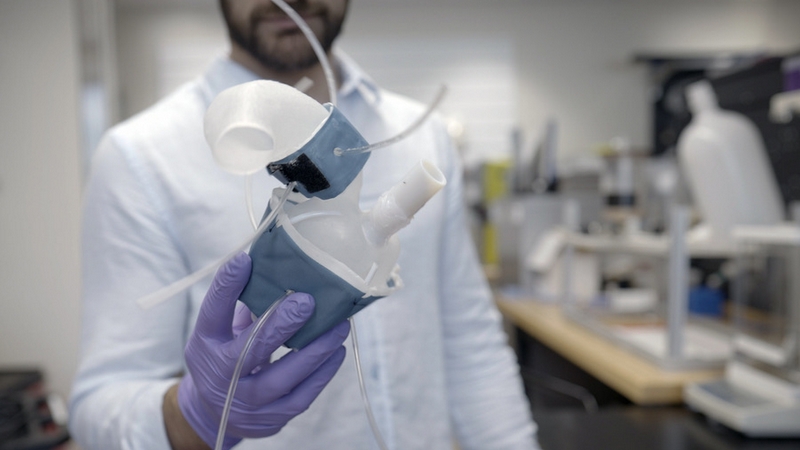

Heart disease is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, and doctors and researchers have been working tirelessly to improve the diagnosis and treatment of this condition. One promising area of research involves the use of 3D printing technology to create personalised models of patients’ hearts, and recently, MIT engineers have developed a procedure to 3D print soft and flexible replicas of patients’ hearts and major vessels, with the goal of tailoring treatments to each patient’s specific heart form and function. How can doctors use these custom robotic hearts to treat heart disease more efficiently, what are the potential applications of these 3D-printed hearts in medical research and the medical device industry, and can this technology be used for other organs besides the heart?
Open-Source Hardware News
3d Printing Antennas With Dielectric Resin
The world of 3D printing continues to evolve and push boundaries, and one area where it is showing particular promise is in the creation of RF components for antennas and microwave lenses. Thanks to a dielectric resin developed by Rogers, high-resolution, scalable 3D printing of complex RF dielectric components is now a reality. However, with a litre of the resin costing over $1,800, it may not be the most affordable option for everyone. Can this resin be used in other printers, are there alternative, more affordable techniques for creating RF components, and what are the benefits and limitations of using 3D printing for RF components?