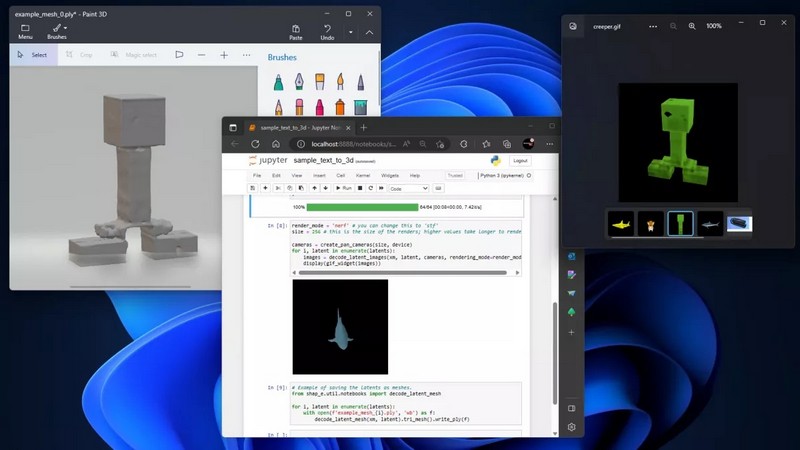
OpenAI, one of the leading artificial intelligence research organizations, has recently developed a new model that can generate three-dimensional (3D) objects from text descriptions or 2D images. This breakthrough is a significant step forward in the field of machine learning, where generating 3D models from natural language or 2D images has been a challenging task. The model, called Shap-E, is a combination of a generative model and a 3D shape predictor. It can create realistic 3D objects with a high degree of accuracy, providing a new level of control and creativity to users. How does the Shap-E model generate 3D objects from text or images, what are the limitations of the current technology, and what are the potential applications of this breakthrough in various industries?
Top Stories This Week
- OpenAI Shap-E Model Makes 3D Objects From Text And Images
- The Rise Of Automotive Semiconductors: A 290B Euros Market By 2030
- To Meet EV Demand, Industry Turns To Technology Long Deemed Hazardous
- Utility-Scale Solar Installation Goes Automated
- OSU Leading $5M Effort To Accelerate Robotics Research Via Standardize Robot
- Artificial Intelligence Helping Recycling Center Sort Waste
- Researchers Hope This Tiny Wearable Could Become Smell-O-Vision For VR
- Do Robots Really Pay For Themselves?
- MIT Engineers Develop Atomically Thin Transistors On Silicon Chips
- First Wearable Health Sensor For Monitoring Muscle Atrophy
- Fairphone’s User-Repairable Headphones Will Offer Spare Parts Through Its App
Hardware Business News
The Rise Of Automotive Semiconductors: A 290B Euros Market By 2030

For the past three decades, automotive semiconductor device manufacturers were considered as the “pedestrian” of the global chip-making community as other application markets like communications and computing dominated sales. However, this is changing, and automotive chipmakers are about to see a big reward, with the global demand for automotive semiconductor devices set to grow significantly, reaching a CAGR of 8.3% or higher. The Asia-Pacific region is expected to be the highest growth market for automotive chips, and the current market value of global car electronics is estimated to be worth €290 billion by 2030. Who are the main players in the automotive semiconductor market, how will technological developments in gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) shape the future of automotive electronics, and what other driving forces are pushing the growth of the automotive electronic devices market?
To Meet EV Demand, Industry Turns To Technology Long Deemed Hazardous

The rise in demand for electric vehicles (EVs) has spurred the search for metals that go into producing EV batteries. Nickel, a crucial ingredient in EV batteries, is primarily sourced from Indonesia, and is home to the world’s largest reserves. To harness these reserves, Indonesia is turning to a refining technology that is environmentally hazardous and has never been used before in the country. Though Indonesia is betting on this technology to drive the country’s future, many experts warn of the environmental costs that come with it. What are the potential environmental impacts of this technology, how will it affect local communities’ lives and livelihoods, and what does Indonesia’s decision mean for the EV industry’s transition away from fossil fuels?
Utility-Scale Solar Installation Goes Automated
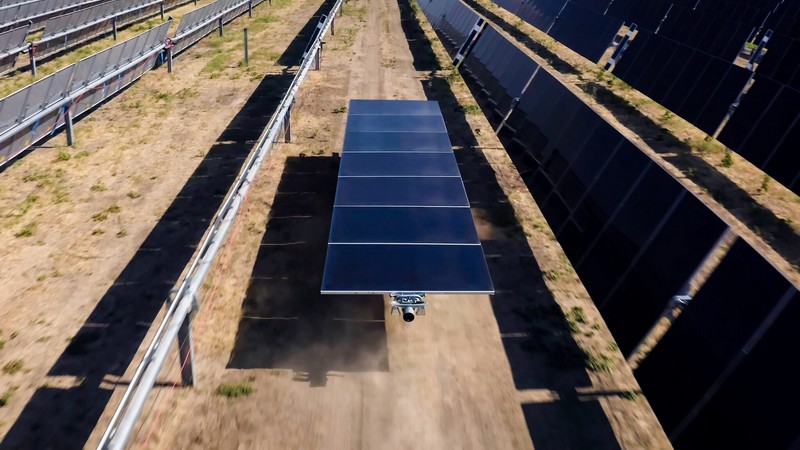

Terabase Energy, a California-based renewable energy company, has announced the launch of an automated utility-scale solar installation system called Terafab. The company claims the system can double installation productivity and reduce physical safety risks for workers by utilizing automation on a climate-controlled assembly line. Terafab is built on a modular design that can be replicated and deployed quickly and is scalable, with the capacity to make more than 10 GW of Terafabs per year, and the system also reduces the levelized cost of electricity for utility-scale solar projects. How can automation help address the solar industry’s labour shortage, how will Terafab impact the future of utility-scale solar installations, and will Terafab’s automation technology become a model for other renewable energy sectors?
OSU Leading $5M Effort To Accelerate Robotics Research Via Standardize Robot
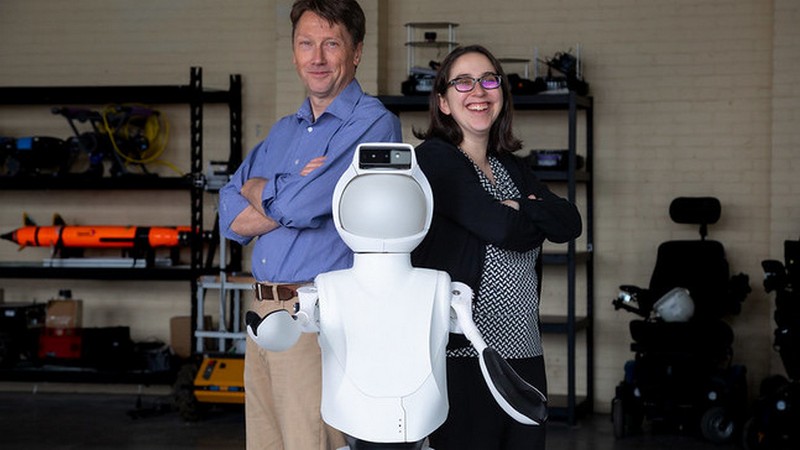

Researchers at Oregon State University (OSU) are part of a $5 million National Science Foundation (NSF) project aimed at accelerating robotics research by providing standardized humanoid robots to the scientific community. Led by Bill Smart and Naomi Fitter, who studies human-robot interaction in the OSU College of Engineering, the project involves building and distributing 50 Quori robots to serve as a standardized hardware and software platform for researchers. The robots, which have expressive faces, gesturing arms, and bowing spines, are designed for experimentation in the lab and real-world types of settings. What is the goal of the NSF’s Computer and Information Science and Engineering Community Research Infrastructure program, how will the standardized Quori robot help accelerate progress in the field of human-robot interaction, and how will the project team increase the diversity of people involved in robotics research in the United States?
Hardware Engineering News
Artificial Intelligence Helping Recycling Center Sort Waste

Recycling is an essential technology in the fight against waste, but while many follow the strict rules on waste organisation, there are still massive quantities of incorrectly sorted bins that can disrupt recycling efforts. At a recycling center in Boulder, Colorado, automation and artificial intelligence are becoming part of the process to help sort recycling waste while also identifying waste that cannot be recycled. In this video, find out how the new system has been deployed and the benefits that it has provided to the recycling center.
Researchers Hope This Tiny Wearable Could Become Smell-O-Vision For VR
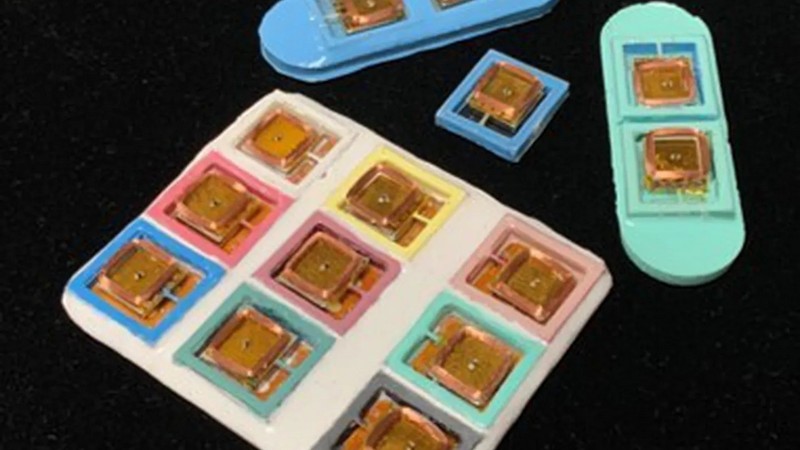
Virtual reality (VR) has come a long way in recent years, with current headsets able to simulate vision, sound, and touch, however, scent has proven to be a challenge to recreate in virtual environments. A team of researchers from Beihang University and the City University of Hong Kong may have found a solution with the development of wearable odour generators that can create up to 30 different scents, including rosemary, mojito, pancake, pineapple, and even durian. The generators, which contain scented wax that can be heated quickly to release a localized scent, come in two formats: a wearable that attaches under the nose and a soft mask. The researchers hope their technology could be used to create more immersive experiences in video games or 4D films, as well as in virtual teaching environments. What challenges do they still face in making this technology practical, how might this technology be used in fields beyond entertainment, and what other solutions are being developed to incorporate scent into VR?
Do Robots Really Pay For Themselves?
Industrial robotics solutions have been gaining traction in the aerospace and defense (A&D) manufacturing industry due to their potential to improve productivity and efficiency while reducing labour costs. However, companies must also account for the initial cost of purchasing and installing these automated systems, as well as conducting a risk assessment to ensure compliance with Robotic Industry Association (RIA) safety standards. How can robotics reduce costs and increase efficiency in A&D manufacturing, what are some examples of successful implementation of industrial robotics in A&D manufacturing, and what are the potential long-term benefits of investing in industrial robotics in A&D manufacturing?
Hardware R&D News
MIT Engineers Develop Atomically Thin Transistors On Silicon Chips

As the semiconductor industry continues to push for more powerful processors to meet the demands of modern applications such as AI, researchers from MIT have developed a new low-temperature growth and fabrication technology for atomically thin transistors that could potentially result in denser and more powerful chips. However, there are still potential limitations and roadblocks that need to be addressed, such as improving the uniformity of the grown layers and integrating these transistors into the underlying semiconductor wafer. In this article, we will explore the challenges faced by semiconductor manufacturers and the potential of this new technology. What are the benefits of growing atomically thin transistors on top of pre-existing silicon dies, what are the limitations and roadblocks that need to be addressed, and how can this technology potentially address the challenges faced by semiconductor manufacturers?
First Wearable Health Sensor For Monitoring Muscle Atrophy
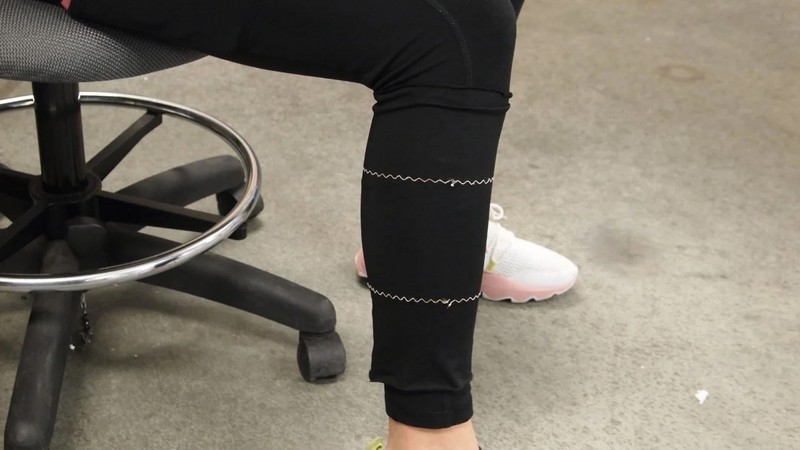

Physicians often rely on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess muscle atrophy in patients, but frequent testing can be both time-consuming and costly. However, researchers at The Ohio State University have developed an electromagnetic sensor made of conductive “e-threads” that could be used as an alternative to frequent MRI monitoring. The sensor could measure small-scale volume changes in overall limb size and monitor muscle loss of up to 51%. The wearable is still years away from implementation, but the researchers are looking forward to integrating the sensor with other devices for detecting and monitoring health issues. In this article, we explore the researcher’s work in more detail and their future plans. How does the technology work, and what were the biggest technical challenges the team faced, what are the next steps for further research, and what advice do the researchers have for engineers aiming to bring their ideas to fruition?
Open-Source Hardware News
Fairphone’s User-Repairable Headphones Will Offer Spare Parts Through Its App
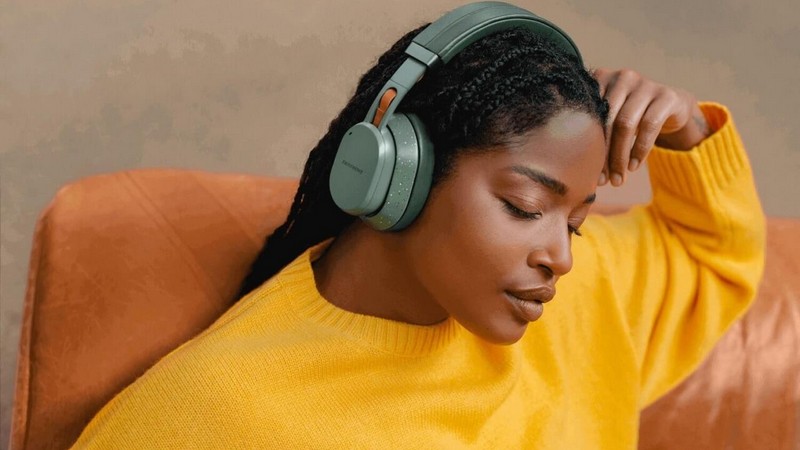

Fairphone, a company that designs sustainable smartphones, has announced the release of its first pair of modular and user-repairable wireless headphones, called the Fairbuds XL. The headphones have a modular design, with spare parts easily accessible, including a headband cover, cable, and left and right speaker modules. The headphones are made using recycled plastic and aluminium and fake leather and are available in green and black. However, Fairphone is unsure how long it will have parts in stock and has reduced its warranty from five to two years. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the Fairbuds XL and answer some key questions. How much do spare parts cost? Can users replace the battery themselves? And will the Fairbuds XL stand the test of time?