Firearms play an essential role in society, whether it’s defence, police, or hunting, but while they can be highly beneficial, they also carry some serious risks to personal safety. Recently, a Colorado-based company, Biofire, has been developing a Smart Gun that utilises biometrics to allow only authorised users to discharge the weapon. This article explores the challenges firearms face concerning safety, how Biofire plans to use biometrics to address these issues, and the potential disadvantages of smart guns.
Top Stories This Week
- Can Biofire’s Biometric Smart Gun Prevent Unauthorised Use Of Firearms?
- US Aims To Tackle Risk Of Uncontrolled Race To Develop AI
- nano3Dprint Unveils 20-Nanometer 3D Print System
- Apple And Google Team Up On Industry Spec To Make Bluetooth Tracking Devices, Like AirTag, Safer
- Sodium-Ion Batteries: The Next Revolution In Energy Storage?
- Why Many “AI-Based” Automation Prototypes Will Never Be Launched
- Predictive Software Could Help Integrate Renewables, Reduce Need For Storage
- New Wearable Device Helps Evaluate The Stiffness of Human Tissue
- The Future Of Soft Robotics: Biodegradable Artificial Muscles & Their Applications
- Charles Lohr Turns A $0.10 RISC-V Microcontroller Into A “Software-Defined Flyback” For Nixie Tubes
Hardware Business News
US Aims To Tackle Risk Of Uncontrolled Race To Develop AI

The US government has stated that firms developing AI are responsible for ensuring their products are safe before deployment and that unchecked AI development could threaten jobs, infringe data privacy and increase the risk of fraud. In response, the government has pledged $140m to invest in seven new national AI research institutes that prioritise ethical, trustworthy, responsible and public-good AI advances. Leading AI developers have also publicly agreed to evaluate their systems at a cybersecurity conference. What are the potential risks to society as AI development continues to accelerate, and how can they be mitigated? How can private companies ensure the safety and security of their AI products, and what role should governments play in regulating AI development? Should there be a moratorium on deploying new generative AI technologies until the risks have been thoroughly assessed?
nano3Dprint Unveils 20-Nanometer 3D Print System
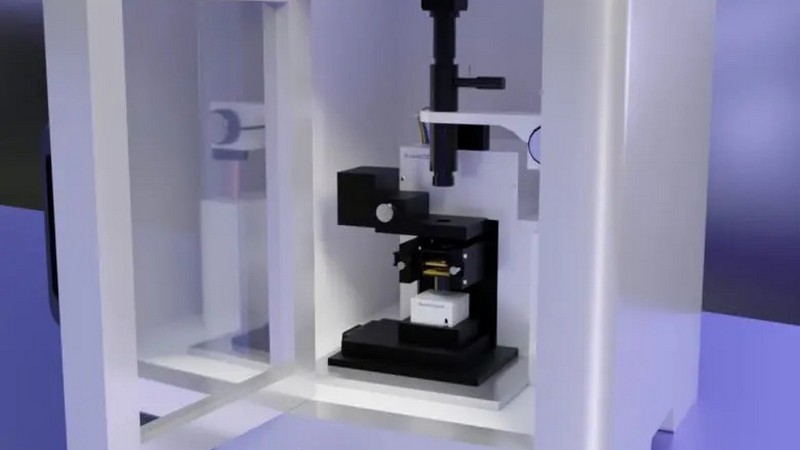

Nano3Dprint, a cutting-edge additive manufacturing solutions provider, has announced the launch of its revolutionary D4200S printer that utilises scanning probe nanotechnology to create nano-scale 3D printing. The D4200S offers unparalleled precision and versatility, capable of printing functional materials for a wide range of applications, including electronics, bioprinting, R&D, and industrial applications. The printer’s advanced capabilities include AFM analysis, nano-writing, and patented 3D printing technology, making it a powerful tool for top-tier research labs and innovative start-ups alike. How does the D4200S differ from other 3D printers on the market? What kind of materials can it print? What impact will it have on the future of additive manufacturing solutions?
Apple And Google Team Up On Industry Spec To Make Bluetooth Tracking Devices, Like AirTag, Safer

Apple and Google have joined forces to develop an industry-wide initiative aimed at curbing the misuse of Bluetooth trackers like Apple’s AirTag. The companies have submitted a proposed specification as an Internet-Draft via a standards development organisation, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), which they hope will offer users more safety measures and combat unwanted tracking across iOS and Android platforms. With Tile and other tracker makers also expressing interest, the initiative aims to create a universal standard that protects users from the misuse of trackers. What are the specifications proposed by Apple and Google, how will the new initiative combat unwanted tracking across different platforms, and what impact will this industry-wide action have on Bluetooth tracking devices’ misuse?
Hardware Engineering News
Sodium-Ion Batteries: The Next Revolution In Energy Storage?

Sodium-ion (Na-ion) batteries have a lot of promise and join the list of the other metal-ion batteries that have not yet made it to the commercial heights of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. However, as more and more people use lithium, there may come a point where resources become scarce, and other technologies need to be available as alternatives. There’s a lot of potential for sodium-based batteries due to the low cost of sodium, the abundance of sodium deposits, and the ability to create batteries with a high energy density if some of the current issues are ironed out. In this article, learn the in’s and out’s of sodium-ion batteries, and their potential role in the future.
Why Many “AI-Based” Automation Prototypes Will Never Be Launched
The development and implementation of artificial intelligence in products can be challenging, particularly if teams set unrealistic goals for automation. Often, teams will use the “Wizard of Oz” technique, in which a product that is supposed to be controlled by AI is actually controlled by a human behind the curtain. However, such a product may never make use of AI, instead relying on humans indefinitely, which is a sad outcome for AI enthusiasts. To avoid this, teams must be honest about their product’s capabilities and start small, automating only certain parts of a user flow. This approach allows teams to build a product that provides value for users without involving humans in the loop. How can teams avoid the trap of the “Wizard of Oz” technique when implementing AI, what are some strategies for starting small with AI automation, and how can we assess the value of an AI product?
Predictive Software Could Help Integrate Renewables, Reduce Need For Storage

The transition to a renewable energy economy poses challenges for managing the mismatch between peak demand and peak generation in an electric system. One proposed solution is the use of utility-scale battery energy storage systems, but a new study from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory suggests an alternative approach using forecast-aided predictive control algorithms to shift demand. The study analysed the use of such algorithms to autonomously control electric vehicle charging stations and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in buildings. However, the study also found that the algorithm’s performance is sensitive to forecast accuracy and decreases during weekends with less flexible demand. This article raises the question of how effective forecast-aided predictive control algorithms can be in shifting demand and reducing the amount of energy storage required in transitioning to a renewable energy economy.
Hardware R&D News
New Wearable Device Helps Evaluate The Stiffness of Human Tissue
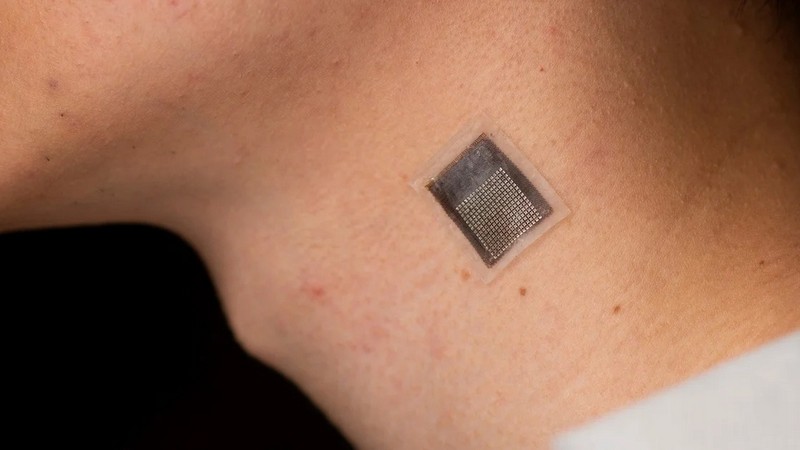
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a stretchable ultrasonic array that provides serial, non-invasive, three-dimensional imaging of tissues as deep as 4 cm below the surface of human skin at a spatial resolution of 0.5 mm. This technology, which is non-invasive and offers enhanced penetration depth, has various applications in the medical field, such as tracking the advance of diseases like cancer, diagnosis and treatment of sports injuries, and monitoring liver fibrosis and myocardial ischemia. This article will discuss how this wearable device works, its specifications, and how it could drive a transformation in the healthcare monitoring field.
The Future Of Soft Robotics: Biodegradable Artificial Muscles & Their Applications

A team of researchers has developed a new artificial muscle that is wholly composed of biodegradable materials, leading the way to compostable robotic systems. Soft robotics is an area that involves designing robots using soft, flexible materials. However, this field presents a unique set of engineering challenges that must be overcome to create practical soft robotic systems. Some of these challenges include designing soft actuators, integrating sensors and feedback systems, power and energy management, and developing suitable materials and manufacturing processes. The new artificial muscle is an actuator made entirely of sustainable materials, and it can flex for over 100,000 cycles without breaking. What did the researchers develop, and how could it be helpful for future applications?
Open-Source Hardware News
Charles Lohr Turns A $0.10 RISC-V Microcontroller Into A “Software-Defined Flyback” For Nixie Tubes
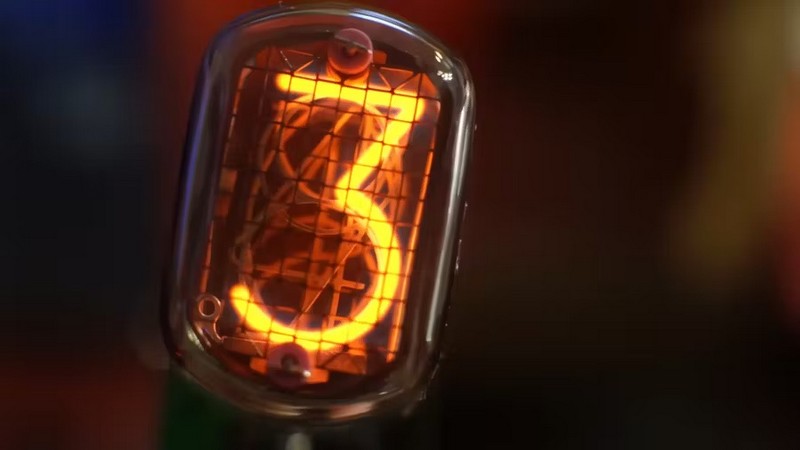

YouTuber Charles Lohr has developed a clever and cost-effective way to drive Nixie display tubes using an ultra-low-cost RISC-V microcontroller. Lohr’s project involves using a CH32V003 microcontroller from WCH Electronics, which has a 40MHz RISC-V processor, 16kB of flash memory, 2kB of RAM, DMA, and many peripherals. This tiny part can even run at 5V, making it perfect for driving Nixie tubes, which require a 180V power supply. Lohr’s project uses the microcontroller to control a closed-loop software-defined flyback power supply, which produces the necessary voltage at a cost of under $0.50 in parts. In this article, we will explore Lohr’s project and how it works, and we will ask: What is a Nixie tube, and how does it work? How does Lohr’s microcontroller-based power supply work? And how can this technology be used in other projects?