In what can only be described as completely surreal, a team of researchers from South Korea have recently made their findings on a new material public, claiming that it’s the world’s first room-temperature semiconductor that operates at ambient pressure. The breakthrough, if validated, could revolutionize various industries, from power transmission to medical imaging. However, the scientific community remains cautious, awaiting further verification of these extraordinary claims. As the physics community holds its breath, questions arise about the authenticity of the findings and the potential implications if it’s indeed real. What is LK-99, the claimed room-temperature superconductor, what evidence supports the researchers’ claims, and if proven to be real, what are the potential implications and applications of room-temperature superconductors across various industries?
Top Stories This Week
- Room-Temperature Superconductor: Finally a Thing?
- New Biodegradable Circuit Board Aims To Reduce The Environmental Footprint
- IBM Study Reveals How AI, Automation Protect Enterprises Against Data Breaches
- AI Surge Saps Intel CPU Sales
- RISC-V AI Startup Tenstorrent Gets Another $100M Infusion From Samsung And Hyundai
- Bad News: Another Data-Leaking CPU Flaw. Good News: It’s Utterly Impractical
- Turns Out There’s Another Problem With AI – Its Environmental Toll
- The ‘eye2see’ Probe Is An Easy Way To Symbolically Debug A Microcontroller
- Archer Further Enhances Biochip gFET Design For Advanced Sensing
- MIT Researchers Build Wearable Ultrasound Scanner For Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
- Esperanto Merging HPC And ML in Upcoming RISC-V Processor
Hardware Business News
New Biodegradable Circuit Board Aims To Reduce The Environmental Footprint

Infineon Technologies, a leading semiconductor manufacturer, is taking significant strides towards an environmentally friendly future with the introduction of Soluboard®, a cutting-edge recyclable and biodegradable printed circuit board (PCB) substrate. Developed in collaboration with UK start-up Jiva Materials, Soluboard® aims to drastically reduce the carbon footprint of the electronics industry. What are the key features that make Soluboard® different from traditional PCB substrates, how does the water-based recycling process associated with Soluboard® enable higher yields in the recovery of valuable metals, and in what ways is Infineon planning to integrate Soluboard® into the electronics industry?
IBM Study Reveals How AI, Automation Protect Enterprises Against Data Breaches

IBM Security’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report presents compelling evidence that incorporating AI, automation, and threat intelligence into cybersecurity strategies leads to shorter breach lifecycles, reduced breach costs, and enhanced overall security resilience. Based on the analysis of 553 actual breaches occurring between March 2022 and March 2023, the report offers valuable insights for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and their teams, who often face resource constraints and the challenge of safeguarding virtual workforces amidst mounting cyber threats. What were the key findings of IBM’s report regarding the average total cost of a data breach and its trend over the last three years, how does the extensive integration of AI and automation impact the breach lifecycle and cost for organizations, and why are some enterprises hesitant to extensively adopt AI and automation in their cybersecurity strategies, despite the apparent advantages demonstrated in the report?
AI Surge Saps Intel CPU Sales

As artificial intelligence (AI) gains traction in the tech industry, leading chipmaker Intel has experienced a dip in its standard compute offerings due to the growing popularity of AI workloads. The surge in demand for AI accelerators by big cloud customers has shifted their budgets away from general-purpose cloud computing CPUs, impacting Intel’s revenue. However, Intel’s CEO, Pat Gelsinger, remains optimistic about the future of the CPU market, believing that the AI workload will eventually balance out between CPUs and accelerators. How has the rising demand for AI accelerators impacted Intel’s revenue, what is Intel’s approach to addressing the AI accelerator market, and despite concerns from investors, why does Intel’s CEO believe that AI will not pose a significant threat to the CPU market?
RISC-V AI Startup Tenstorrent Gets Another $100M Infusion From Samsung And Hyundai
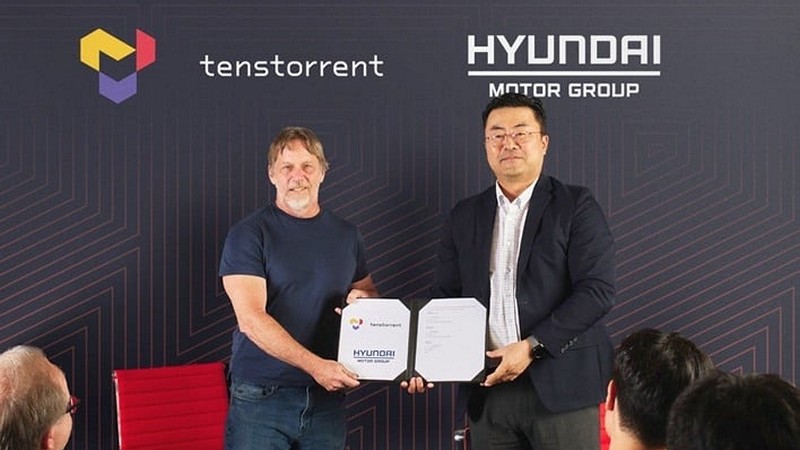

Renowned tech guru Jim Keller’s latest venture, Tenstorrent, a startup specializing in developing high-performance processors based on the RISC-V ISA for AI training and inference, has garnered significant attention and funding. With a remarkable track record in the semiconductor industry, including work on AMD’s K8 processors and the Zen architecture, Keller’s Tenstorrent has already raised over $230 million. The recent $100 million investment from major players like Hyundai Motor Group and Samsung’s Catalyst Fund reflects growing confidence in Tenstorrent’s potential and its role in advancing AI applications, particularly in automotive technology. How does Jim Keller’s extensive background in the semiconductor industry contribute to the interest and investment in Tenstorrent’s AI processor development, what specific advantages does Tenstorrent’s RISC-V ISA-based processors offer for AI training and inference, and how will the new investment from Hyundai and Samsung’s Catalyst Fund accelerate Tenstorrent’s product development and help achieve its goals in the AI processor market?
Hardware Engineering News
Bad News: Another Data-Leaking CPU Flaw. Good News: It’s Utterly Impractical
A team of researchers from Graz University of Technology and CISPA Helmholtz Center for Information Security in Austria and Germany has devised a new power-monitoring side-channel attack on modern computer chips, dubbed Collide+Power. Unlike previous side-channel attacks, this technique utilizes variations in processor power usage to infer the contents of CPU cache memory, potentially exposing encryption keys and sensitive data. How does the Collide+Power side-channel attack differ from traditional side-channel attacks, what are the two variants of Collide+Power, MDS-Power, and Meltdown-Power, and how have AMD, Arm, and Intel responded to the researchers’ disclosure?
Turns Out There’s Another Problem With AI – Its Environmental Toll

As the cryptocurrency craze raised concerns about its environmental impact due to energy-intensive mining, researchers are now turning their attention to the energy footprint of another booming tech industry: AI. Generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT and Google Bard, rely heavily on powerful GPUs for processing, which, like cryptocurrency mining, consume significant amounts of electricity. The environmental cost of AI is difficult to quantify due to limited transparency from companies behind popular AI tools and GPU manufacturers. However, some estimates indicate that training AI models like GPT-3 could consume millions of litres of water and emit hundreds of tons of carbon dioxide equivalent. What are the parallels between the environmental impact of cryptocurrency mining and the energy consumption of AI tools that rely on GPUs, how have researchers attempted to quantify the environmental impact of AI, and what challenges does the AI industry face in striking a balance between maintaining performance and reducing its ecological impact?
The ‘eye2see’ Probe Is An Easy Way To Symbolically Debug A Microcontroller

Debuggers are essential tools for embedded systems engineers, providing real-time insights into device performance and errors. However, traditional debuggers often require additional hardware and pins, adding to the cost and complexity of the debugging process. Mark Henderson’s eye2see project offers an innovative alternative by utilizing the widely available I2C protocol to transmit and receive symbolic debugging information, eliminating the need for extra pins. How does the eye2see project utilize the I2C protocol to enable symbolic debugging without the need for additional pins on the target microcontroller, what are the key components of the eye2see setup, including the eye2see Probe and the py2see application, and what limitations does the eye2see system have in terms of execution times?
Hardware R&D News
Archer Further Enhances Biochip gFET Design For Advanced Sensing
Archer Materials Limited, a semiconductor company specializing in quantum computing and medical diagnostics, has made significant advancements in biochip fabrication. The company has developed a next-generation graphene field effect transistor (gFET) design that allows for single-device multiplexing, enabling the biochip to detect and control multiple diseases from a single chip. This breakthrough is a critical milestone in the commercialization process and could revolutionize disease detection and analysis. What are the key advancements in Archer’s next-generation biochip fabrication, how does the gFET design allow for single-device multiplexing, and how is Archer moving towards a streamlined commercialization model for its biochip technology?
MIT Researchers Build Wearable Ultrasound Scanner For Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
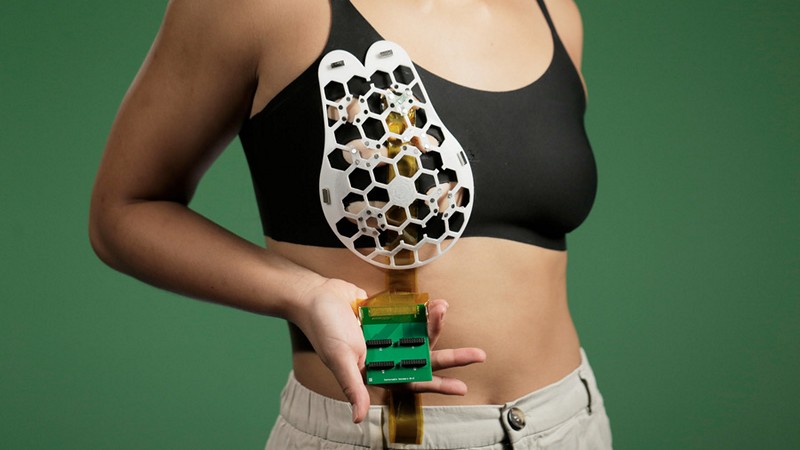

Breast cancer is a leading cause of death among women, and early detection is crucial for improving survival rates. To address this challenge, researchers at MIT have developed a wearable ultrasound device that could allow individuals to detect breast tumours in their early stages. The device, a flexible patch attached to a bra, allows real-time imaging of breast tissue using ultrasound technology. This breakthrough could be particularly beneficial for high-risk patients in between routine mammograms, as it enables more frequent screening. How does the wearable ultrasound device work, what are the potential benefits of using the device for early breast cancer detection, especially for high-risk individuals, and how does the development of this technology align with the goal of improving breast cancer survival rates and increasing access to screening?
Open-Source Hardware News
Esperanto Merging HPC And ML in Upcoming RISC-V Processor

Esperanto Technologies, a company specializing in RISC-V processors, has ambitious plans for its next-generation chip. They aim to create a chip that combines both CPU and GPU capabilities, catering to machine learning and high-performance computing needs. With the flexibility of the RISC-V architecture, Esperanto believes they can achieve this goal and offer substantial performance while maintaining power efficiency. During a presentation at the RISC-V Summit, CEO Dave Ditzel discussed the upcoming ET-SoC-2 chip, which will feature new high-performance CPU cores with RISC-V vector extensions. How does Esperanto’s vision of combining CPU and GPU capabilities on a single RISC-V chip differ from the traditional accelerator model, how does the RISC-V architecture enable Esperanto to target both double-precision computing for HPC and lower-precision computations for machine learning, and how do they plan to achieve energy-efficient performance with the ET-SoC-2?