What is Bead Blasting?
Bead blasting is a surface finishing technique that provides a clean and uniform texture to various materials similar to sandblasting. However, instead of using fine grains of sand, bead blasting uses small spherical beads made from materials such as glass ceramic or metal. These beads are propelled at high speed towards the surface of the item being treated, effectively cleaning it or altering its appearance. This process is particularly useful for removing surface deposits or providing a matte finish to items.
One notable difference between bead blasting and sand blasting is the texture of the finish. Bead blasting often produces a rougher surface compared to sandblasting which can be highly beneficial in applications where enhanced adhesion is needed. For example surfaces prepared with bead blasting provide better adherence for paints and coatings. Similarly in assembly processes where components need to be glued together a bead blasted surface ensures that adhesives hold more securely reducing the risk of failure in the final product.
The versatility of bead blasting comes from the ability to use different types of beads and varying bead sizes. Each bead material offers distinct characteristics glass beads for example are ideal for achieving a smooth satin or matte finish without damaging the underlying material. Ceramic beads are harder and provide a more aggressive cleaning action suitable for tougher contaminants or for preparing metal surfaces for stronger mechanical bonding. The size of the beads also plays a crucial role in determining the finish of the blasted surface; smaller beads are typically used for finer, more delicate finishes whereas larger beads are chosen for a more pronounced rougher finish.
For engineers and professionals looking to utilize bead blasting, a deep understanding of the process and its variations is crucial. Knowing when to use a particular type of bead or bead size can significantly impact the effectiveness of the process. For example selecting the appropriate bead material and size for a specific material or desired finish can enhance the quality and durability of the final product. Engineers must also consider factors such as the blasting equipment air pressure and distance from the nozzle to the surface as these can all influence the outcome of the blasting process.
How Does it Work?
The basic mechanism behind bead blasting is straightforward yet effective. Tiny beads made from various materials such as glass, ceramic, or metal are propelled at high speeds towards a target object, causing a slight deformation of the surface being blasted. This deformation, which is carefully controlled, alters the surface without removing any material, and this is primarily used to finish metal parts to a uniform matte appearance. The process of bead blasting is similar to hammering metal into shape, with each bead acting as a tiny hammer, gently shaping the surface of the part through repeated impact.
The operation of a bead blasting machine is also straightforward, involving a hopper system that stores the beads, which are then directed towards the part using a stream of compressed air. This setup allows for precise control over the intensity and coverage of the blasting process, enabling uniform treatment of the part’s surface. Furthermore, the reusability of the beads makes the process even more efficient, as the beads can be collected and recycled. While the beads can be reused multiple times, their lifespan depends on their material composition, with harder materials being more cost-effective in the long run.
The reusability of the beads not only reduces waste but also reduces the need for new materials, thereby enhancing the sustainability of the process. The combination of precision, efficiency, and environmental benefits makes bead blasting an attractive option for surface treatment in various industrial applications.
What Is It Used For?
One of the primary uses of bead blasting is to clean surfaces by removing accumulated materials such as rust paint or other types of debris. This is particularly beneficial in restoration projects or in manufacturing settings where old parts need refurbishing before they can be reused or repurposed. The beads effectively strip away unwanted layers without damaging the underlying surface which can be a delicate balance to maintain with more abrasive surface preparation techniques.
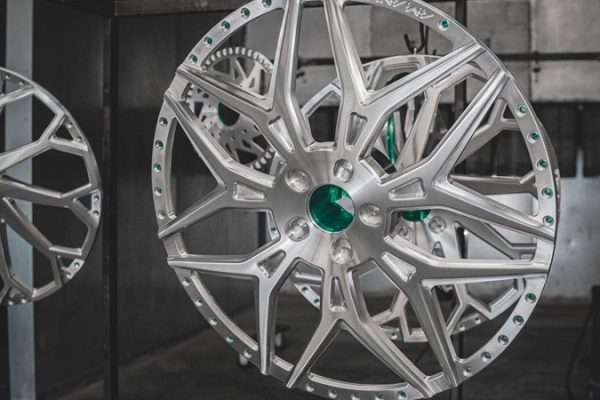
Bead blasting does not create a polished or smoothed finish as some other blasting techniques do, instead, it leaves a pebbled matte texture that is visually appealing and can be functional as well. This texture is not only aesthetically pleasing but can also diffuse light and reduce the visibility of fingerprints and smudges which is particularly desirable in consumer electronics and automotive parts.

The texture achieved through bead blasting can be finely controlled by selecting beads of different sizes; smaller beads will generally produce a finer texture while larger beads create a more pronounced rougher finish. This ability to control the finish is invaluable in applications where precision is key such as in creating non-reflective surfaces on optical equipment or providing a textured grip on tools and handles.
Bead blasting is also excellent for preparing a smooth surface to receive a dull or satin finish as the process effectively etches the surface, increasing its ability to bond with coatings. This is particularly important in industries where coatings need to adhere strongly to the base material such as in automotive and aerospace manufacturing.
Bead Blasting vs. Sandblasting
When it comes to surface cleaning, two primary options exist; bead blasting and sandblasting. Bead blasting uses glass or ceramic beads that are significantly softer than sand, meaning they are considered less aggressive. This gentler nature allows for bead blasting to clean surfaces without removing large amounts of material, something that is particularly important for maintaining the integrity of a surface. As such, bead blasting is ideal for applications that require a high degree of precision and smoothness, such as automotive restorations where original body panels need to be preserved.
On the flip side, sandblasting uses sand as the primary abrasive which is harder and sharper than the beads used in bead blasting. This makes sandblasting significantly more aggressive, capable of removing large amounts of material, and is therefore ideal for removing tough layers that cannot be removed with bead blasting. One common example of sandblasting in restoration includes the removal of rust from metal that has undergone severe corrosion, such as old military equipment that has been in rivers for decades. The extreme rust can be removed using sandblasting, revealing the underlying metal.
However, the extreme nature of sandblasting also means that it is not suitable for applications that require a high degree of precision and smooth finish, such as aerospace components and some automotive parts. Furthermore, the rough finish left by sandblasting can also be problematic in applications that require a smooth surface, such as precision machinery and equipment.

In contrast, the smooth finish provided by bead blasting makes it ideal for these applications, but its gentle nature also means that it is less capable of removing tough layers of rust and debris. Thus, bead blasting is ideal for applications that require a high degree of smoothness and precision, while sandblasting is ideal for applications that require a high degree of material removal, such as restoration projects where rust and debris need to be entirely removed.
Bead Blasting Materials
Glass beads are a popular choice due to their ability to be recycled, and their relatively gentle nature means they do not damage surfaces easily. As such, they are ideal for cleaning metal surfaces without removing too much of the underlying material, and their ability to impart a bright finish makes them ideal for automotive and aerospace applications.
Aluminum oxide, however, is ideal for more aggressive cleaning and surface preparation. It’s hard nature makes it effective at removing surface layers and smoothing out rough textures, which is why it is often used to prepare surfaces for painting and anodizing. Its abundance and low cost also make it an economical choice for heavy-duty applications, which is why it is commonly found in automotive and manufacturing industries.
Softer beads, such as plastic, are ideal for applications that require a gentle cleaning process. Their inability to cause damage makes them ideal for restoring automotive bodies and delicate parts, which is why they are also used in automotive industries. The inability of plastic beads to contaminate other media also makes them ideal for use in controlled environments.
Pumice is another material that is commonly used in bead blasting, and its rough texture makes it ideal for removing surface imperfections and preparing metal for further processing. The natural origin of pumice also makes it an eco-friendly option for those looking to reduce their environmental impact, which is why it is also becoming popular in organic and biodegradable applications.
Finally, steel shot is ideal for the most extreme applications that require an extremely aggressive cleaning process. Unlike other media, steel shot is able to remove heavy layers of rust and scale, as well as being able to leave a high-quality finish. This makes steel shot ideal for refurbishing heavy machinery and equipment, as well as for use in construction and building industries.
Best Practices for a Perfect Bead Blast
While the bead blasting process itself is handled by our manufacturing experts, understanding the desired outcome of your part’s appearance is essential as this will directly influence the choice of bead size used in the blasting process.
However, it is also essential to reassess whether bead blasting is the most suitable method for your needs. While bead blasting is excellent for achieving a uniform, clean, and attractive surface, other techniques such as regular polishing or brushing might be adequate depending on the finish you require. These alternatives could be preferable if you are looking for a simpler or less abrasive finish, so comparing these methods before deciding on bead blasting can save time and resources.

The environmental impact of the manufacturing process is also becoming increasingly important, and if your project demands an eco-friendly approach, then consider opting for organic bead materials that are biodegradable and can be composted. This not only helps to reduce the environmental footprint but also aligns with green manufacturing practices that are becoming standard in the industry.
Precision is also a critical factor, especially for components that must meet strict dimensional tolerances. In such cases, using finer, softer bead materials can be advantageous as smaller beads provide a gentler abrasion which results in a more consistent and precise surface finish. This is particularly important in industries where the smoothness of a part’s surface can affect its performance, such as aerospace or medical devices.
Key Takeaways
Bead blasting is a surface finishing technique that uses small beads propelled at high speed to clean or polish the surface of a material. Unlike sandblasting, which uses coarse materials to aggressively remove contaminants and coatings, bead blasting is a gentler process that achieves a smooth, uniform finish, similar to a satin finish. This makes bead blasting ideal for applications that require a high degree of aesthetics, such as in automotive, aerospace, and architectural projects, where the smooth finish helps to reduce the adherence of dirt and grime, thereby prolonging the life of the part. The smooth finish also enhances the visual appeal of the metal, making it suitable for applications where appearance is crucial.
Compared to sandblasting, bead blasting is less aggressive and therefore less likely to damage the underlying material. While sandblasting is effective in removing tougher coatings and preparing surfaces for painting or other treatments, it can create a rougher finish, making it unsuitable for applications that require a smooth surface. The gentler nature of bead blasting also makes it ideal for delicate materials that could be damaged by more aggressive methods, such as sandblasting.
The choice of beads used in the blasting process is critical to achieving the desired outcome. Various materials, such as glass, ceramic, and plastic, are available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, glass beads are excellent for imparting a clean, bright finish without causing dimensional changes to the workpiece, while ceramic beads are harder and more suitable for tougher cleaning jobs, although they can be more abrasive. Plastic beads are the gentlest option and ideal for softer materials that could be damaged by other bead materials.
When selecting beads for a specific application, it is essential to consider the type of finish required and the characteristics of the material being blasted. Each type of bead material provides a unique type of finish and has a different impact on the material being blasted, so choosing the right beads for the job is crucial. Using the wrong type of bead can result in surface damage or dimensional changes, which is why careful consideration must be given to this selection process.
By carefully choosing the right beads and blasting technique, manufacturers and restorers can effectively utilize bead blasting to enhance the appearance and longevity of their products. The ability of bead blasting to achieve a high-quality finish while removing contaminants and preparing surfaces makes it an ideal process for a wide range of applications, from new manufacturing processes to restoration projects.
Why Choose Ponoko
Choosing a manufacturer for your next prototype or production part can be a daunting task as numerous considerations and potential pitfalls need to be addressed. The process of selecting a manufacturer requires extensive research and comparison to ensure that a reliable partner is found who can meet all the specific needs. Even after a manufacturer is chosen, concerns such as turnaround time, quality of the finished product, and assurances from the manufacturer can continue to be a source of worry.
The complexity of the selection process increases when considering that some manufacturers may not be able to handle all aspects of production, including material sourcing, manufacturing, finishing, and shipping. The logistics involved in coordinating with multiple vendors can lead to increased costs and extended timelines, making it a stressful experience for those needing a manufacturer capable of handling all stages of production.
However, for those who are losing sleep over such challenges, Ponoko offers a comprehensive solution that simplifies the entire production process from start to finish. By integrating all steps of manufacturing under one roof, Ponoko eliminates the need for coordinating with multiple suppliers, thereby reducing the likelihood of errors and saving valuable time.
The confidence that Ponoko has in its quality is evident in its customer-centric policies, including a 365-day money-back guarantee for every part manufactured. This bold guarantee underscores their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, providing clients with peace of mind knowing that Ponoko is fully accountable for the products delivered.
Our approach is holistic and customer-focused, taking responsibility for the entire lifecycle of the products we make. By choosing Ponoko, businesses can alleviate the typical stresses associated with product manufacturing and focus on innovation and growth, secure in the knowledge that their manufacturing needs are in capable hands.


