A team of scientists led by Dr. Darius Viržonis from Kaunas University of Technology (KTU), Lithuania, has developed ground-breaking gravimetric sensors capable of detecting greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane with exceptional sensitivity. These gravimetric gas sensors represent a significant leap forward in gas detection technology, offering heightened sensitivity and reduced energy consumption compared to traditional electrochemical sensors. What distinguishes gravimetric gas sensors from traditional electrochemical sensors, how do these differences enhance their effectiveness in detecting greenhouse gases, and how might gravimetric sensors be applied in health research, particularly in the diagnosis of viral diseases?
Top Stories This Week
- Researchers Develop Sensor That Reduces The Price Of Greenhouse Gases Detection
- Qualcomm Turns To Samsung For 2nm Process
- Startup Emerges From Stealth With $25 Million For Robots That Lay Bricks As Fast As Humans
- France Announces New Export Controls On Semiconductors, Quantum Equipment, And Technology
- Apple Breaking iPhone Web Apps In The EU
- Justice Department Conducts Court-Authorized Disruption of Botnet Controlled By Russia
- Google And EDF To Track Methane Leaks From Space
- Beyond Silicon: A Look At Alternative Chip Materials
- Oxford PV Claims Record For Perovskite-Silicon Solar Panel
- Wearable Device Could Help Predict Preterm Birth
- Microchip’s Low-Cost PolarFire SoC Discovery Kit Makes RISC-V And FPGA Design More Accessible
Hardware Business News
Qualcomm Turns To Samsung For 2nm Process

In a strategic maneuver aimed at securing cutting-edge chip technology, Qualcomm, a leading mobile application processor company, has turned to Samsung Electronics for the development of a ground-breaking 2nm application processor (AP). This move follows Apple’s surprising acquisition of TSMC’s entire first run of 3nm chips in 2023, leaving Google’s Pixel 8 Pro smartphones with a less advanced 4nm processor from Samsung. How does Qualcomm’s collaboration with Samsung for 2nm chip development reflect the escalating competition in the semiconductor industry, particularly in light of Apple’s strategic moves, what factors will determine the success of Samsung and TSMC in mass-producing 2nm semiconductors, and how might this impact Qualcomm’s decision-making process?
Startup Emerges From Stealth With $25 Million For Robots That Lay Bricks As Fast As Humans
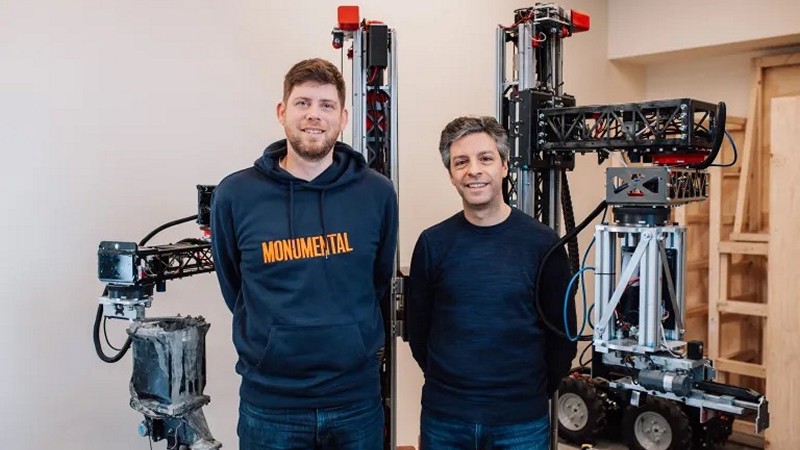

The shortage of skilled bricklayers is a significant challenge in the construction industry, impacting housing projects across Europe and the U.S. To address this issue, Monumental, an Amsterdam-based start-up, has unveiled a new generation of bricklaying robots. These robots, equipped with AI technology and innovative robotic parts, aim to revolutionize the construction sector by offering an efficient and cost-effective alternative to human bricklayers. How might Monumental’s robotic bricklayers redefine the traditional approach to construction efficiency and workforce dynamics, in what ways could the widespread adoption of robotics in construction impact job opportunities and skill requirements in the industry, and considering Monumental’s success, what implications does this hold for the future integration of AI in construction technologies?
France Announces New Export Controls On Semiconductors, Quantum Equipment, And Technology
Effective March 1, 2024, France will enforce stringent export regulations on technologies associated with quantum computers and advanced electronic components, such as semiconductors, destined for non-EU countries. These measures, enacted via the Export Controls Order 02-2024, align with recent initiatives by neighbouring EU nations like the Netherlands and Spain and reflect the EU’s broader How might France’s export controls on quantum technologies and advanced semiconductors impact global trade dynamics and technological innovation in these sectors, what steps should companies operating in the advanced technologies and quantum industries take to ensure compliance with France’s export regulations, and what implications might arise for other EU Member States5?
Apple Breaking iPhone Web Apps In The EU

Apple has made a significant decision to cease support for progressive web apps (PWAs) for iPhone users located within the European Union (EU). Despite previous indications of web app dysfunction in iOS 17.4 beta versions, Apple has now clarified that this cessation is an intentional move rather than a technical glitch. How will Apple’s decision to discontinue support for progressive web apps impact the accessibility and functionality of web-based services for iPhone users in the European Union, what implications might Apple’s assertion regarding security risks associated with alternative browser engines and web apps have on the broader debate surrounding digital privacy and regulatory compliance, and what does this reveal about the evolving preferences of consumers and the challenges faced by developers in the app ecosystem?
Hardware Engineering News
Justice Department Conducts Court-Authorized Disruption of Botnet Controlled By Russia

In a significant cybersecurity operation, the FBI has dismantled a Russian botnet that exploited vulnerabilities in hundreds of home Wi-Fi routers. According to the Justice Department, the botnet, utilizing the Moobot malware, originated from installations by non-GRU cybercriminals on Ubiquiti Edge OS routers. What specific tactics and techniques did the Russian botnet employ to compromise home Wi-Fi routers, how significant is the involvement of Russia’s GRU Military Unit 26165 in repurposing the botnet for intelligence-gathering purposes, and what measures can individuals and organizations take to protect their home Wi-Fi routers and devices from similar cyber threats in the future?
Google And EDF To Track Methane Leaks From Space

Google has joined forces with the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) in an innovative partnership aimed at combating methane emissions by harnessing satellite technology. This collaboration leverages Google’s advanced AI capabilities and infrastructure mapping alongside EDF’s MethaneSAT satellite to identify and locate sources of methane emissions from outer space. How does the MethaneSAT satellite differentiate itself from previous methods of monitoring methane emissions, what role does Google’s AI and cloud computing infrastructure play in enhancing the capabilities of MethaneSAT, and how does Google plan to utilize AI and satellite imagery to create a global map of oil and gas infrastructure?
Beyond Silicon: A Look At Alternative Chip Materials

Since its inception in 1954, silicon has been the cornerstone of modern technology, serving as the foundation for our electronics infrastructure. However, as technology continues to evolve guided by Moore’s law, the limitations of silicon have become increasingly apparent. This has spurred the exploration of alternative semiconductor materials that could complement or enhance silicon’s capabilities in various applications. What are the primary advantages of wide-bandgap semiconductor materials such as gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) over traditional silicon, how do these materials enable innovation in power electronics and RF applications, and despite their potential benefits, what are the main challenges hindering the widespread adoption of GaN and SiC, particularly in terms of reliability, cost, and production complexity?
Hardware R&D News
Oxford PV Claims Record For Perovskite-Silicon Solar Panel

Oxford PV, in collaboration with the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems, has achieved a milestone in solar panel efficiency. Their tandem photovoltaic cells, combining perovskite and silicon technologies, have attained a record conversion efficiency of 25%. This remarkable achievement represents a significant advancement in solar energy generation and underscores the potential of perovskite-on-silicon tandem cells to revolutionize the renewable energy industry. What distinguishes Oxford PV’s perovskite-on-silicon tandem photovoltaic cells, how does their record-breaking efficiency of 25% compare to conventional solar panels, and what implications does this hold for the widespread adoption of Oxford PV’s technology and the future of solar energy production?
Wearable Device Could Help Predict Preterm Birth

Preterm birth poses significant health risks for newborns, and predicting it remains a challenge in prenatal care. However, recent research by WHOOP and West Virginia University explores the potential of maternal heart rate variability (HRV) measured through wearable technology as a digital biomarker for preterm birth. This innovative approach offers new insights into predicting delivery dates and facilitating timely interventions to improve maternal and neonatal outcomes. How does maternal heart rate variability serve as a non-invasive indicator of the autonomic nervous system’s activity, why is it particularly relevant for predicting preterm birth, and what are the challenges and opportunities in further research to assess the individual-level utility of monitoring HRV for predicting preterm birth?
Open-Source Hardware News
Microchip’s Low-Cost PolarFire SoC Discovery Kit Makes RISC-V And FPGA Design More Accessible

As the demand for open-source RISC-V-based processor architectures grows within the embedded industry, access to commercially available silicon and hardware remains limited. Addressing this gap, Microchip Technology introduces the PolarFire SoC Discovery Kit, aiming to democratize innovation in embedded processing and compute acceleration. How does the PolarFire SoC Discovery Kit bridge the gap between demand for open-source RISC-V-based processor architectures and the limited availability of commercially available silicon and hardware, what key features and capabilities does the Discovery Kit offer to empower engineers in exploring emerging technologies, and how does this initiative enhance the practical learning experience for students and align academic studies with industry trends in embedded systems and FPGA design?


