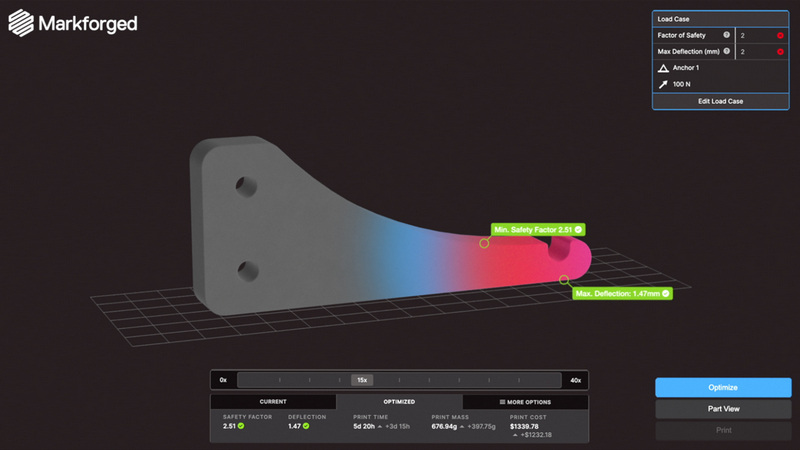
There is no doubt that 3D printers have revolutionised engineering thanks to their ability to provide rapid development cycles, significantly reduce manufacturing costs for low-volume production runs, and even provide the ability for engineers to create complex parts that are no longer manufactured. However, one big challenge that 3D printed parts face is their structural integrity and trying to predict if and how such a part will break. Recognising such challenges, Markforged has recently released simulation software that can help engineers identify mechanical stress in virtually printed parts, and thus determine if a part can be used as a suitable replacement.
Top Stories This Week
- New 3D Printing Software Enables Virtual Testing
- What’s The One Big Reason Why China Will Not Invade Taiwan?
- UK Government Launches £1.5m AI Programme To Tackle Carbon Emissions
- Uber Launches Robotaxi Service In Las Vegas
- Lockheed Martin Explores 3D Printing As Alternative To Castings
- Japan’s Sewer Pipes May Soon Be Crawling With Spider-Like Inspection Robots
- All You Need To Know About Bio-Wearables
- French Hospital Suspends Operations After Cyber Attacks
- Wearable Sensor Could Guide Precision Drug Dosing
- A New Self-Powered Ingestible Sensor Opens Fresh Avenues For Gut Research
- Open-Source IC Architecture Taking Off In China
Custom parts for startups & enterprises - order online, delivered same day.
Hardware Business News
What’s The One Big Reason Why China Will Not Invade Taiwan?

Tensions between Taiwan and China remain high, with Taiwan insisting that it is an independent country while China insists that Taiwan will eventually be reunited with China. But while the rest of the world wonders if and how a conflict might start, others believe that such a conflict will never happen. In this article published on electropages, learn about the history between the two nations, why the author believes that chips are the reason why China would never invade, and where the future of the two nations will lead.
UK Government Launches £1.5m AI Programme To Tackle Carbon Emissions

Reducing carbon emissions globally presents numerous challenges, and expecting all countries to follow the same rules regardless of their economies is unfair, to say the least. But while many look towards reducing fossil fuels and increasing tree populations, others wonder if the very technology resulting from carbon emissions can be the answer to the challenge. With the UK Government’s intention to work towards decarbonisation, a new programme has been launched that will provide £1.5m to fund a new virtual centre of excellence as well as numerous outside AI projects. What challenges does decarbonisation face, what has the government announced, and why could AI be the solution to many challenges faced by mankind?
Uber Launches Robotaxi Service In Las Vegas
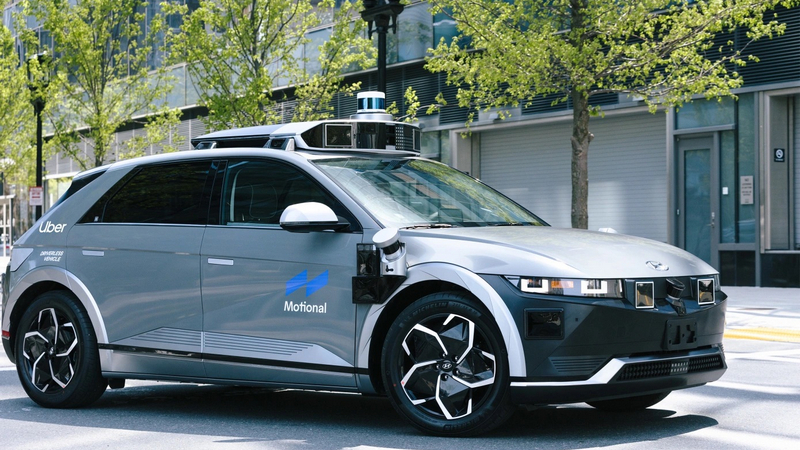

While research continues in the field of autonomous vehicles, no automaker has managed to achieve fully self-driving vehicles. However, some companies have managed to develop vehicles that can safely navigate small areas and specific routes, and Uber has recently announced a new Robotaxi service that operates in Las Vegas. What technical challenges do such vehicles face, where exactly does the service operate, and could it be expanded in the future?
Lockheed Martin Explores 3D Printing As Alternative To Castings
3D printing technologies have dominated the prototyping industry thanks to the ability for 3D printers to print custom designs, low print costs, and minimised material waste. While using 3D printed parts in a market product is certainly possible, it doesn’t scale well for mass production, nor do 3D printed parts have the same structural integrity as those made using forged metal or injected moulded plastic. Now, Lockheed Martin is exploring the use of 3D-printed parts to replace forged and cast parts. What challenges do 3D printed parts face, why is Lockheed Martin exploring 3D printing, and could it become a viable manufacturing technique in the future?
Talk with an expert
Hardware Engineering News
Japan’s Sewer Pipes May Soon Be Crawling With Spider-Like Inspection Robots

Japan’s ageing population combined with its workforce moving towards services, finding workers willing to do demanding jobs is becoming more difficult. To make matters worse, Japan’s sewer pipes have a life expectancy of 50 years and were installed almost 50 years ago, meaning that replacement work will soon need to be done. As there are few workers willing to crawl into sewer systems, engineers in Japan are developing robotic systems that will do the job for them. What challenges does Japan’s workforce face, what have the researchers developed, and will robotics replace humans in demanding jobs?
All You Need To Know About Bio-Wearables
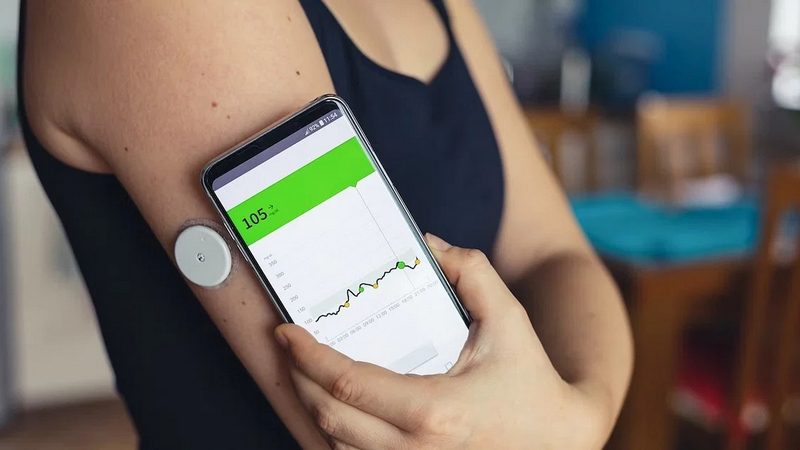

As the wearable market continues to grow, there are some very real arguments to be made for wearable medical monitors, also known as bio-wearables. From general monitoring of health to detecting sudden emergencies, wearable medical devices can provide numerous advantages to users, and this is especially true after the challenges faced by society during the COVID pandemic. In this article published by the Free Press Journal, learn what bio-wearables are, the advantages they present, and the challenges they face.
French Hospital Suspends Operations After Cyber Attacks
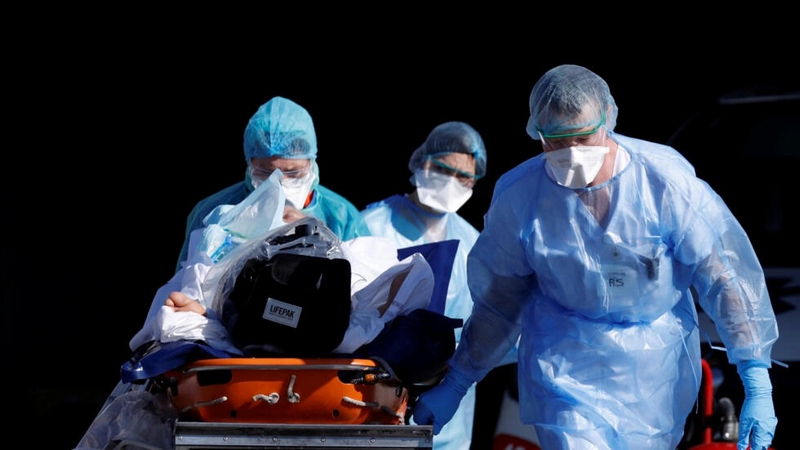
Technology has enabled countless advances in the sciences, and the integration of electronics and computational devices into everyday life has become so great that life simply cannot exist without such devices. But now that most aspects of life are connected to the internet in some shape or form, they are vulnerable to cyberattacks, and a recent cyberattack on a French hospital forced a complete shutdown of all services. What challenges does technological integration into modern life present, why did the hospital shut down, and could this become a recurring challenge?
Hardware R&D News
Wearable Sensor Could Guide Precision Drug Dosing
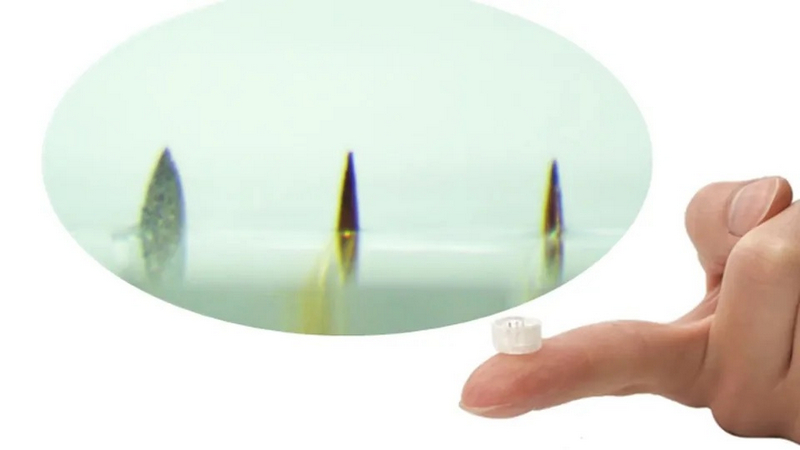
For some of the powerful drugs used to fight infection and cancer, there’s only a small difference between a healing dose and a dose that’s large enough to cause dangerous side effects. But predicting that margin is a persistent challenge because different people react differently to medications – even to the same dose. Now, a UCLA-led research team has developed a wearable patch that uses inexpensive microneedles to analyze the fluid between cells less than a millimetre underneath the skin and continuously record concentrations of medicine in the body. What challenges does drug delivery face, what did the researchers develop, and how could such technology change the future of treatment?
A New Self-Powered Ingestible Sensor Opens Fresh Avenues For Gut Research
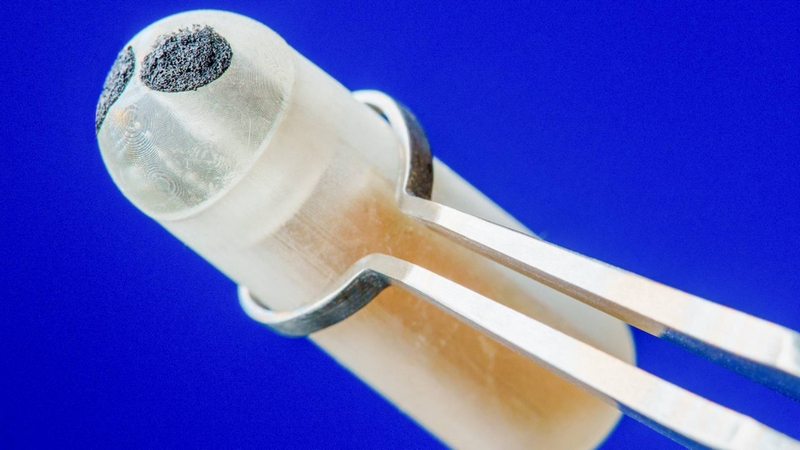
Trying to diagnose issues inside the body can prove to be challenging without the use of invasive methods. While internal body scans can be made, they rarely have the ability to show issues such as bleeding, sores, and ulcers. Now, engineering researchers have developed a battery-free, pill-shaped ingestible biosensing system designed to provide continuous monitoring in the intestinal environment. What challenges do current diagnostics methods face, what did the researchers develop, and how will it aid future medical research?
Open-Source Hardware News
Open-Source IC Architecture Taking Off In China
The numerous technology bans against China by the West continue to put China in a difficult spot as the latest technologies (including semiconductors) are needed to stay economically and militarily competitive. But the developments in RISC-V are now seeing China move away from Western technologies in favour of open-source projects, and it is very likely that the future of China will be entirely based on Western open-source designs. What challenges does China face, why is China adopting RISC-V, and could it be the solution for China looking long-term?