Researchers have achieved a significant breakthrough by unveiling Brainoware, a hybrid biocomputer that seamlessly blends laboratory-grown human brain tissue, specifically brain organoids, with traditional electronic circuits. Described in the journal Nature Electronics, this innovative technology holds the potential to revolutionize artificial intelligence (AI) and advance neuroscience research. How might the integration of brain organoids with electronic circuits in Brainoware contribute to the development of more efficient and powerful AI systems, what challenges and ethical considerations should be addressed in the further development and potential deployment of Brainoware, and in what ways could Brainoware potentially replace animal models in studying the brain’s function and neurological disorders?
Top Stories This Week
- Biocomputer Combines Lab-Grown Brain Tissue With Electronic Hardware
- EU Agrees AI Rules In Historic Deal
- Tesla Unveils Optimus Robot Gen 2
- TSMC Confirms That Mass Production Of 2nm Processors Will Begin In 2025
- Intel 3D Stacked CMOS Transistors Combine Backside Power & Direct Backside Contact To Deliver Increased Performance
- Spectre-Based Attack Exploits Intel, Arm, And AMD CPUs
- Europol Raises Alarm On Criminal Misuse Of Bluetooth Trackers
- Revolutionising Traffic & Access Control With AI And Edge Computing
- Wireless Tech Could Replace Bluetooth At Short Distances And Boost Battery Life 5-Fold
- Cellulose Could Replace Plastics In Flexible Electronics
- OSHWA Updates Hardware Licensing Guidelines
Hardware Business News
EU Agrees AI Rules In Historic Deal

After an exhaustive negotiation process spanning over 36 hours, European Union negotiators have successfully reached an agreement to establish the world’s first comprehensive laws regulating artificial intelligence. The ground-breaking AI Act, championed by European Commissioner Thierry Breton, represents a significant leap in global AI governance. How does the EU’s two-tiered system position the region in relation to other global players like the US, the UK, and China in terms of AI regulation, what specific challenges and opportunities does the tiered system present for AI developers, and with differing opinions on the regulation of foundation models, as seen in the negotiations involving France, Germany, and Italy, what impact might the EU’s AI Act have on the broader landscape of AI development and the global debate on the ethical use of artificial intelligence?
Tesla Unveils Optimus Robot Gen 2
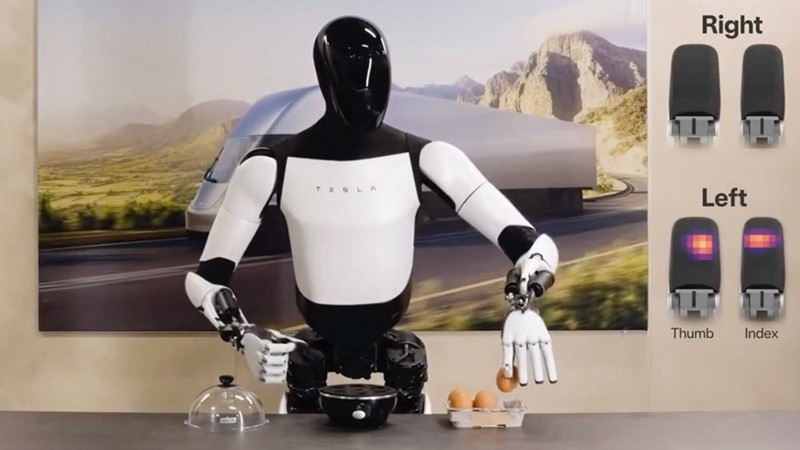

In a recent video update, Tesla has showcased the remarkable progress of its humanoid robot, Optimus Gen 2. The latest iteration represents a substantial evolution from its predecessor, boasting enhanced design, improved functionality, and a display of human-like movements. With the Optimus Gen 2’s impressive hardware improvements, particularly in tactile sensing and delicate object manipulation, what industries and practical applications do you envision for Tesla’s humanoid robot beyond its potential use in assembly lines, what steps does Tesla need to take to ensure the reliability and flexibility of Optimus in real-world tasks, and how might the advancements made in FSD software contribute to the success of Optimus Gen 2 in situations with fewer variables, such as repetitive tasks in various industries?
TSMC Confirms That Mass Production Of 2nm Processors Will Begin In 2025

In a race to power the next generation of smartphones, datacentres, and artificial intelligence, semiconductor giants are fervently developing 2 nanometre processor chips. Leading this charge is TSMC, a dominant force in the global processor market, who has confirmed the commencement of mass production for its ‘N2’ process in 2025, with Apple poised to be its lead customer. How might this announcement impact the competitive landscape among semiconductor manufacturers, what potential applications could benefit the most from these advancements, and what steps are TSMC and other semiconductor companies taking to overcome these challenges and ensure a smooth transition to the 2nm process technology?
Intel 3D Stacked CMOS Transistors Combine Backside Power & Direct Backside Contact To Deliver Increased Performance

Intel has showcased ground-breaking advancements in semiconductor technology at the 2023 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, revealing its next-gen 3D Stacked CMOS Transistor technology. This innovation leverages backside power and direct backside contacts to achieve superior performance and scaling on upcoming chips. How will this breakthrough impact the performance and efficiency of next-gen chips, what potential applications could benefit the most from these advancements, and what challenges does Intel face in achieving this goal, particularly in terms of backside power delivery and the integration of novel materials?
Hardware Engineering News
Spectre-Based Attack Exploits Intel, Arm, And AMD CPUs

In a significant revelation, researchers have identified a novel type of side-channel attack known as Spectre based on Linear Masking (SLAM), capable of bypassing the security measures of the latest CPUs. Leveraging a memory feature that stores untranslated data bits in the kernel metadata, SLAM can extract sensitive information, including encryption keys and root passwords. How exactly does the SLAM side-channel attack exploit the memory features of CPUs, what specific vulnerabilities in the Linear Address Masking (LAM), Top Byte Ignore (TBI), and Upper Access Ignore (UAI) security features make CPUs susceptible to this form of transient execution-based attack, and what role do software patches, like those released by Linux, play in mitigating the risks posed by SLAM and similar side-channel attacks?
Europol Raises Alarm On Criminal Misuse Of Bluetooth Trackers

Europol has raised alarms over a new trend in organized crime, revealing that criminals are increasingly utilizing Bluetooth trackers for illegal activities, primarily in the geolocation of illicit commodities. Originally designed for personal item tracking and vehicle theft prevention, these small devices have now become tools of choice for drug traffickers, with a focus on cocaine smuggling. How do criminals exploit Bluetooth trackers to facilitate the geolocation of illegal commodities, particularly in the context of cocaine smuggling, what specific challenges do law enforcement agencies face in detecting and preventing the use of these devices in organized crime, and how can regulatory and technological measures be implemented to mitigate the potential misuse of Bluetooth trackers in organized crime activities?
Revolutionising Traffic & Access Control With AI And Edge Computing

The Perini Business Park in Brazil is undergoing a technological evolution through a collaborative effort involving SKIDATA, ASUS IoT, and Manica DHW. This alliance aims to automate and enhance the access control and parking management systems of the business park, marking a significant step in its transition into a technologically advanced hub. How does the integration of edge computing, IoT, and AI contribute to optimizing parking management and enhancing the overall user experience, what challenges and opportunities does it present for design engineers seeking to enhance the functionality and efficiency of large-scale commercial spaces, and how can collaborative engineering efforts between companies like SKIDATA, ASUS IoT, and Manica DHW set benchmarks for the future of smart city development?
Hardware R&D News
Wireless Tech Could Replace Bluetooth At Short Distances And Boost Battery Life 5-Fold

Scientists have developed a new wireless technology, Electric Potential Sensing Communication (EPSComm), that has the potential to rival Bluetooth by consuming significantly less power. Unlike traditional wireless technologies relying on electromagnetic field modulation, EPSComm utilizes electric field modulation, reducing power consumption on receiving devices, and the technology has been to use demonstrated to use 10 times less power than Bluetooth in experiments. How does EPSComm differ from traditional wireless technologies, in what ways can EPSComm be integrated into wearable and mobile devices, and how could a dual-technology approach impact the user experience?
Cellulose Could Replace Plastics In Flexible Electronics

As electronics become thinner and more flexible, there’s a growing concern about the environmental impact of using plastics in manufacturing. A team of researchers in Italy is addressing this issue by exploring cellulose, the main component of plant cell walls, as a sustainable alternative to plastics in flexible electronics. How does cellulose, specifically its derivatives such as ethyl cellulose and hydroxypropyl cellulose, offer a sustainable alternative to conventional plastics in the manufacturing of flexible electronics, what properties make them suitable for this purpose, and what are the potential applications of sensors using these new materials?
Open-Source Hardware News
OSHWA Updates Hardware Licensing Guidelines
In response to the evolving landscape of hardware licensing and the growing popularity of the CERN Open Hardware Licence v2, the Open Source Hardware Association (OSHWA) has updated its guidelines on sharing hardware designs efficiently. The most significant change is the introduction of four distinct licensable elements for open hardware: hardware, design files, documentation, and software. How does the adoption of version 2 of the CERN Open Hardware Licence influence the changes in OSHWA’s hardware licensing guidelines, what makes this license particularly suitable for sharing hardware designs, and how do the reciprocal variants of CERN OHL v2 fill the gap in licensing for FPGA or ASIC designs using Hardware Description Languages?

