Our injection molding capabilities
Our injection molding service enables you to go from just 1 to 1 million parts. We have a minimum lead time of 15 days, a maximum part size of 480x751x203mm, a dimensional accuracy of ±0.08mm, and we conform to ISO-9001, ISO-13485, and ITAR standards. We offer 100+ thermoplastic and thermosetting materials, which makes our service ideal for many applications, including industrial, medical and consumer.
Injection molding tooling capabilities
Designing and manufacturing molds is a complex process as numerous factors need to be considered including the mold material, expected yield, and the budget. To help engineers with this process, our software-driven injection molding services come with a mold designed by our in-house engineers. Thus, you only need to focus on designing your product, deciding how many you need, and what material you require.
We offer 3 tooling options, to fit the stage of your product’s development:
Alpha Prototype Tool
Lead time
Part quantity
Max parting line mismatch
Max flash
Linear dimensional tolerance
Part color
Part finish - color
Part finish - texture
Beta Prototype Tool
Lead time
Part quantity
Max parting line mismatch
Max flash
Linear dimensional tolerance
Part color
Part finish - color
Part finish - texture
Production tool
Lead time
Part quantity
Max parting line mismatch
Max flash
Linear dimensional tolerance
Part color
Part finish - color
Part finish - texture
Injection molding thermoplasitcs capabilities
Our plastics injection molding capabilities vary depending on the type of mold used, the part material used, and the tolerance needed for the part. While injection molding is ideal for precision applications, it is essential that you read and understand the tolerances and specifications stated in the table below to ensure that all parts fit together. For example, a 5mm hole with a tolerance of ±0.05mm may struggle to fit on a metal rod with an equal diameter and similar tolerance as it is possible for the rod to be larger in size than the hole.
Min lead time
Size
Volume
Depth
Mold area
Tolerance - machining
Tolerance - resin
Thermosets injection molding capabilities
Our silicone rubber injection molding process takes advantage of aluminum molds for low-cost fabrication as well as a fast part turnaround of 15 days minimum. With a build area of 304.88mm x 203.2mm x 101.6mm and machining tolerances of ±0.08, our silicone rubber injected parts are ideal for both prototypes and precision applications.
Min lead time
Size
Volume
Depth
Mold area
Tolerance - machining
Tolerance - linear
What is injection molding?
Injection molding is an additive manufacturing process that injects molten material under high pressure into a mold. Compared to other manufacturing processes, injection molding is by far the fastest due to the high speed at which material is injected into molds and the quick cooling time for parts coming out of molds.
While the entire injection process time depends on the complexity of a part and its size, this cycle can be as fast as 2 seconds and as long as 2 minutes. Suppose a mold is designed to hold multiple copies of a design. In that case, the production yield of each cycle is multiplied, and this is why it is a favorite amongst engineers when manufacturing parts.
Our injection molding services are perfect for engineers needing to scale up their production, and our software-driven solutions not only reduce the complexities involved with injection molding but also remove the need for engineers to design and order molds.
Our injection molding materials
We have 100+ thermoplastic and thermoset materials for you to select from …
Injection molding thermoplastic materials
Thermoplastics are plastics that become pliable when heated, allowing them to be reheated multiple times without degrading. This makes thermoplastics excellent for recycling applications as they can be ground down and reused, but this ability also makes them more resistant to fatigue. Common examples of thermoplastics include PLA, acrylic, polyester, nylon, and Teflon, and applications for these materials include storage units, medical parts, food processing, consumer goods, and electrical equipment. Thermoplastic options include:
| Commodity grade ($) | Engineering grade ($$) | High performance grade ($$$) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystalline plastics | Polypropylene (PP) Polyethylene (PE) High density polyethylene (HDPE) Low density polyethylene (LDPE) | Polyoxymethylene (POM / Acetal) Polyamide (PA / Nylon) Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | Perfluoroalkoxy (PFA) Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) |
| Amorphous plastics | Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) Polystyrene (PS) Polycarbonate / Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (PC/ABS) Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA / Acrylic) Polyethylene terephthalate glycol (PETG) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) | Polycarbonate (PC) Polyurethane (PUR / PU) | Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU / Radel R®) Polyetherimide (PEI / Ultem®) Polysulfone (PSU) |
Imidized plastics ($$$$)
Polyamide-imide (PAI) Polybenzimidazole (PBI) Polyimide (PI) |
Elastomer plastics
Santoprene Kraton Estane Pellethane Hytrel Sarlink Polytrope Elastollan Dynaflex |
Injection molding thermoset materials
Thermosetting plastics are those manufactured from polymer liquids that harden when cured via heating. Once cured, these plastics are extremely strong and typically heat resistant, but unlike thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics cannot be reheated, and this means they are very difficult to recycle. But this inability to recycle makes them excellent for applications requiring extreme durability such as chemical-resistance and long-term stability.
Common examples of thermosetting plastics include epoxy, silicone, polyurethane, and phenolic, and common applications for such materials include gas and water pipes, automotive parts, medical equipment, construction, electrical fittings, and kitchen appliances.
Thermoset rubber options include:
- Standard silicone (30, 40, 50, 60, and 70 durometers)
- Medical-grade silicone
- Optical-grade silicone
- Fluorosilicone (fuel and oil resistant)
How does cloud manufacturing work?
Over the past 200 years, the field of manufacturing has undergone massive changes, whether it was the introduction of steam, electricity, and automation. But while all of these technological changes have helped to increase production rates and improve the quality of manufacturing, there are still numerous challenges that engineers have to face, including the orchestration of complex industrial facilities, securing supply chains, checking for defects in equipment and finished parts, and tracking changes in designs throughout development.
To help engineers with this, Ponoko fully utilizes cloud manufacturing technologies that help simplify the entire manufacturing process by separating design engineers from production. In addition to shielding engineers from the complexities of the manufacturing process, we also provide software-driven tools that provide instant price estimates to engineers. These pricing tools enable engineers to make rapid costing decisions in hours instead of having to wait days for quotes from multiple suppliers.
Finally, our cloud manufacturing technologies connect all the suppliers and needed logistics to a singular network that provides real-time communication. Thus, orders placed using our cloud technologies instantly alert material suppliers, logistics, and engineers to ensure a rapid manufacturing process.
How much does an injection mold cost?
By far, the biggest cost factor in injected molded parts is the mold, and this is due to their large size, the engineering needed to make them, and the complexities in their design. As stated previously, molds are complex to make as material needs to fill all cavities at a uniform rate, molds require specific channels for venting and pressure regulation, and the mold itself needs to be able to withstand massive pressures.
The price range for injection molds varies from around $1.5K to $100K where the lower-end prices are for simple molds made from aluminum. Expensive molds are made from high-grade stainless steel, which is designed to produce millions of parts, and while such molds may be expensive, their price is insignificant when considering the combined value of millions of parts.
The type of material chosen will also alter the tolerances provided by the mold due to the differences in metal hardness. For example, low-cost aluminum molds are easier to machine due to aluminum being a relatively soft metal, and this results in tolerances of around ±0.1mm. By contrast, stainless steel molds can have tolerances down to ±0.02mm as stainless steel can maintain its structure well during machining (i.e., it’s not prone to tearing). Additionally, smaller tolerances require increased machining time and precision tools which are far more expensive to use.
As such, aluminum molds are an excellent candidate for rapid prototyping where only a handful of parts are required, whereas stainless steel molds are excellent for use in mass production. Furthermore, stainless steel is also ideal for applications where a great deal of precision is needed (such as the medical and aerospace industries).
Our injection molding prices include the mold, and we provide all the services needed to design, manufacture, and select the most suitable options for the mold. This means that design engineers can spend more time focusing on the design of your part and the features you need, while we use our manufacturing expertise to create all the supporting materials needed to manufacture that part.
How we guarantee quality molded parts at speed
All our molded parts come with a 365-day guarantee that provides engineers with a high degree of reliability. Furthermore, this guarantee applies no matter the order quantity meaning that large-scale orders requiring fast manufacturing times are still protected. This requires Ponoko engineers to carefully tune manufacturing processes to identify the best manufacturing speeds that do not compromise the final quality of plastic-injected molded parts.
In addition to our 365-day guarantee, our services have been used by 33,000+ engineering customers and have manufactured over 2 million parts for use in numerous industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical and IoT.
What parts are good for injection molding?
Injection molding is an excellent manufacturing method for parts that need to be produced in bulk, requiring a high degree of accuracy. While the initial cost for an injection mold can be relatively large, the ability to rapidly turn around 10,000 (or 500k) parts makes injection ideal for mass-produced products. Injection molding is arguably one of the most popular manufacturing processes worldwide.
Parts that can take advantage of injection molding include fittings, enclosures, brackets, and mounts. Parts made from thermoplastics that need to be recycled can also do well with injection molding as they can not only be fully recycled but can be made from recycled materials.
With respect to applicable industries, there are very few industries that injection molding cannot cater for. For example, medical devices can utilize thermosetting plastics for hygienic enclosures, IoT devices can use thermoplastics for creating enclosures, and EV automotive applications can take advantage of specialized materials such as glass-filled nylon for providing electrical insulation.
Injection molding is widely used for plastic part production in medical, industrial, consumer and automotive industries. Typical parts include:
- Housings
- Brackets
- Gears
- Single-use medical parts
- Electrical connectors
- Syringes
- Containers
- Televisions
- Remote controls
- Printers
- Electrical circuit boards
- Cell phones
- Toothbrushes
- Cosmetic packaging
- Helmets
- Jewel boxes
- Padding
- Syringes
- Knobs
- Intake manifolds
- Beakers
- Test tubes
- Medical implants
- Fixtures
- Vents
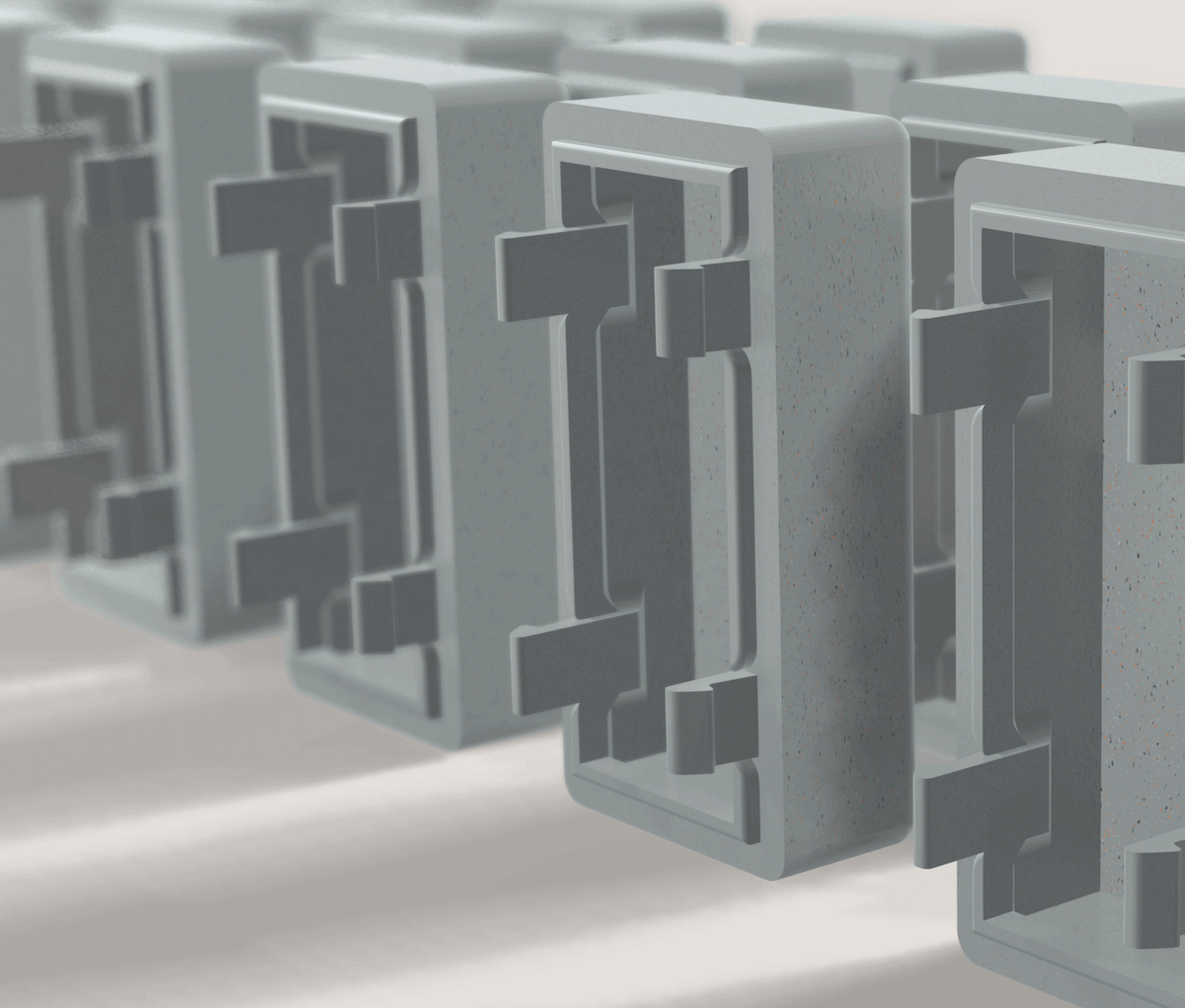
Snap fits and other mechanical action parts
One common use for injection molded parts is mechanical fittings that require no additional processing. While enclosures and parts can be joined using screws, brackets, and bolts, these add complexity to the final part, and incur additional manufacturing costs. Instead, engineers often adopt the use of snap fittings that take advantage of plastic flexibility to create strong reusable clips. These clips are easy to insert but nearly impossible to pull apart (unless the clip is bent back), and this can be used to create self-latching enclosures and clips that require no tools to use. Such clips are integrated into the design of a part, and thus can be plastic injected molded.
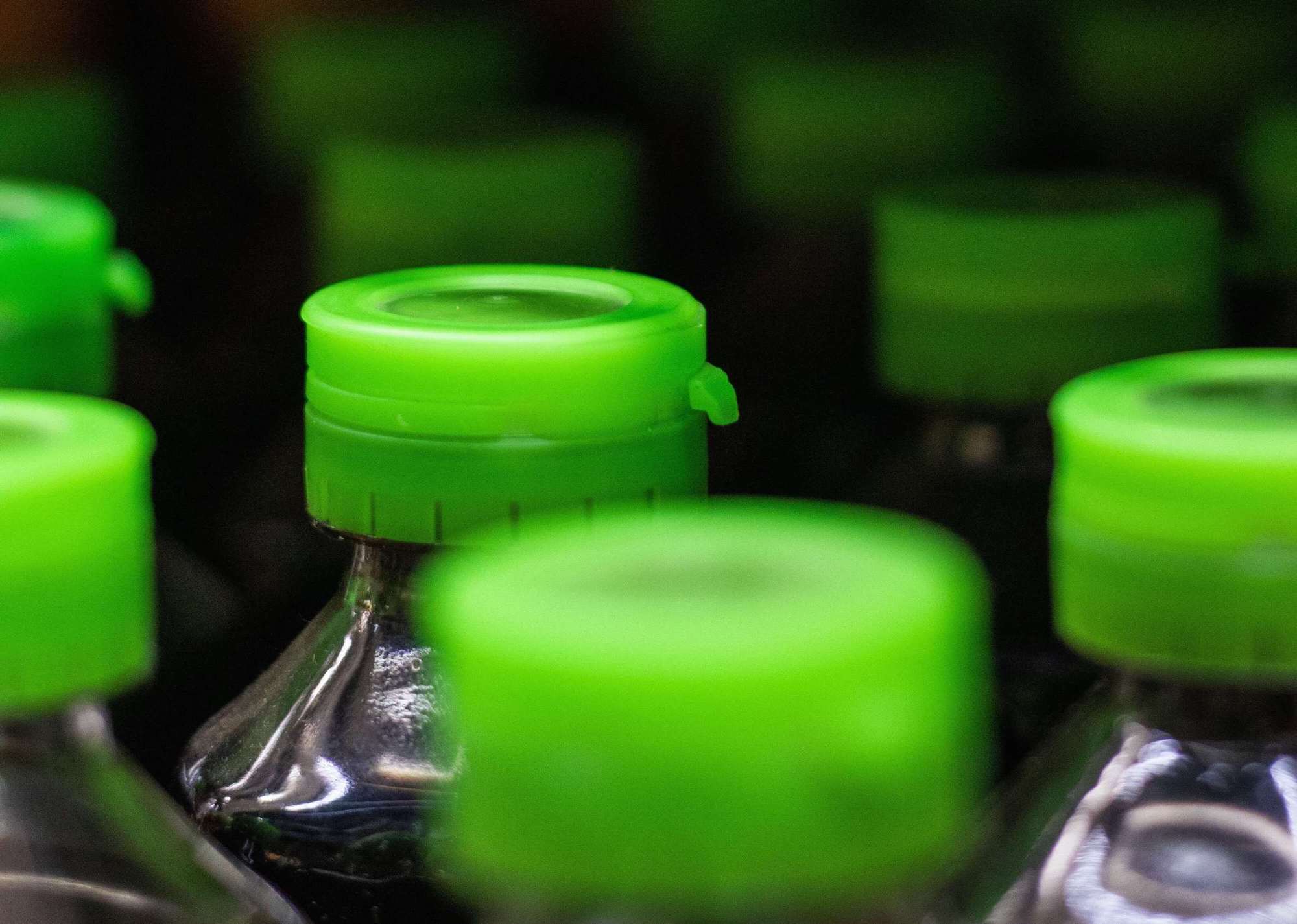

Living hinges
Many mechanical designs require some kind of movement between two parts, and while this can be achieved with the use of hinges and bearings, they are expensive to use, and the labor needed to install them can drive up manufacturing costs. Trying to add mechanical action to low-cost parts produced in the millions makes traditional mechanical options impractical. One solution that engineers have been using for decades is the living hinge, a piece of flexible plastic between two parts that enables movement. Not only do living hinges entirely eliminate the need for hinges, but they can enable two separate parts to be integrated into a single mold, thus simplifying manufacturing.
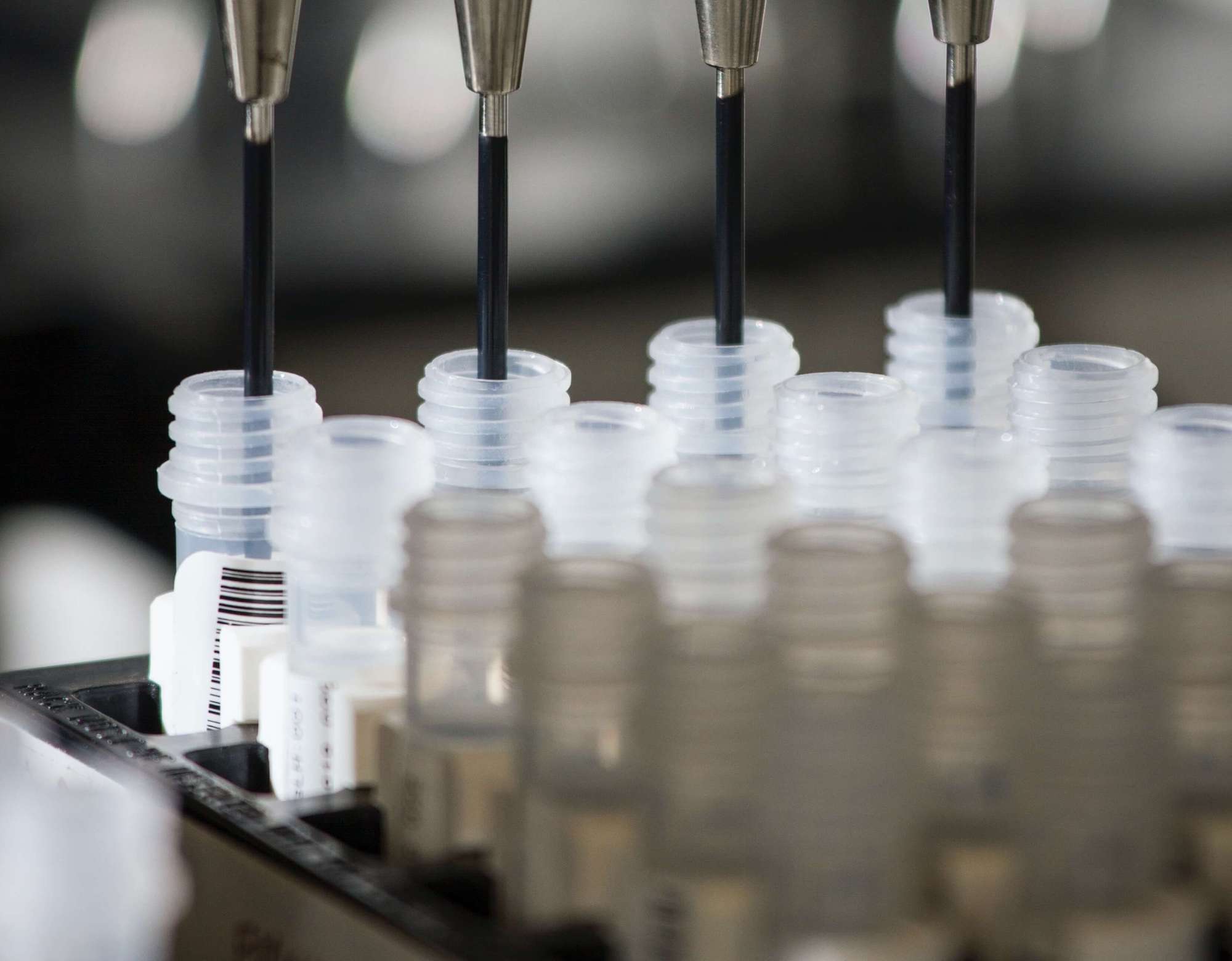

Medical equipment
The medical industry is another industry that heavily relies on injection molding thanks to the extremely low costs offered when producing at large volumes. As large portions of medical equipment are single-use only (to prevent cross-contamination), cheap plastics are needed for taking samples, treating patients, and providing protective equipment. One such example has been rapid COVID tests that utilize injection molding to create the hundreds of millions of enclosures used by the testing strip as well as the swab.
Why choose our service?
The need for custom molds and time-consuming machine configuration introduces numerous risks to designers, especially if placing orders in the tens of thousands. For this reason alone, Ponoko is an excellent option for those looking for injection molded parts as our years of experience with over 33,000 customers ensures that the part you need manufacturing will be done so at the highest degree of quality while simultaneously being able to identify potential problems before they manifest in the final part (such as design incompatibility with injection molding).
Another benefit to using Ponoko injection molding services is that we deploy industry-leading security practices to protect intellectual property. Manufacturing injected molded parts en-masse can be daunting, but no engineer should have to worry about entrusting their design files to a manufacturer. Thus, Ponoko provides engineers with a manufacturing service that not only has strict quality assurances on all parts, but also offers a level of security and trust that’s hard to beat.
Plastic Injection molding FAQ
What are the four stages in injection molding
What advantages does injection molding offer
What disadvantages does injection molding present
Is injection molding cheap
Need something different? Try our other services…
Injection molding is great, but it’s not always the best service to use, especially for prototypes. If you are looking for parts in low volumes, or want to avoid committing to large, expensive molds, then consider one of our many other manufacturing services.
Laser cutting is excellent for those needing 2D parts as laser cutting is not only cheap (thanks to the lack of molds and tools), but also incredibly accurate. For those needing 3D plastic parts, our range of 3D printing services can also be extremely beneficial, and the additive nature of 3D printing makes it a very cost-effective solution for complex shapes. And of course, if you are looking for electronic circuits, then you should definitely check out our full PCB production services that not only fabricate PCBs, but fully populate them too.